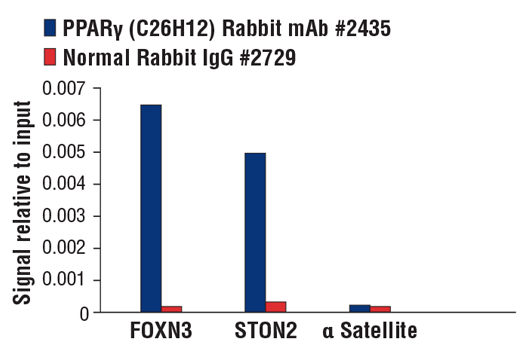
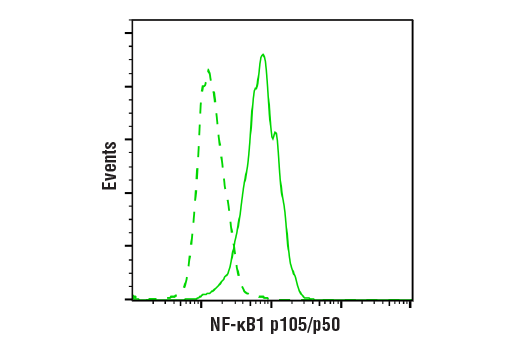
| Product Includes | Product # | Quantity | Mol. Wt | Isotype/Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
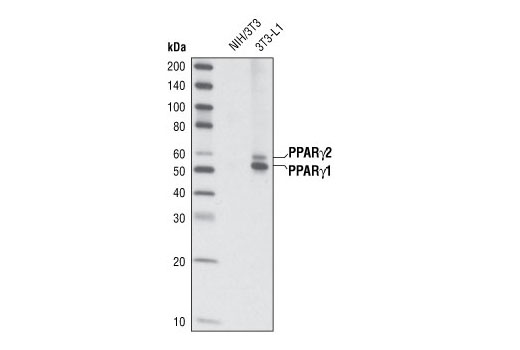
| PPARγ (C26H12) Rabbit mAb | 2435 | 20 µl | 53, 57 kDa | Rabbit IgG |
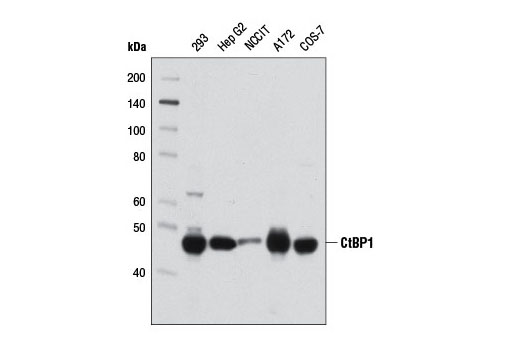
| CtBP1 (D2D6) Rabbit mAb | 8684 | 20 µl | 47 kDa | Rabbit IgG |
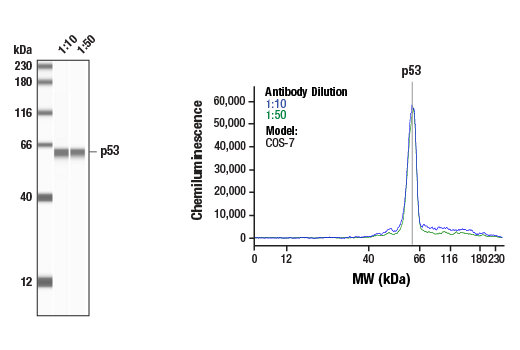
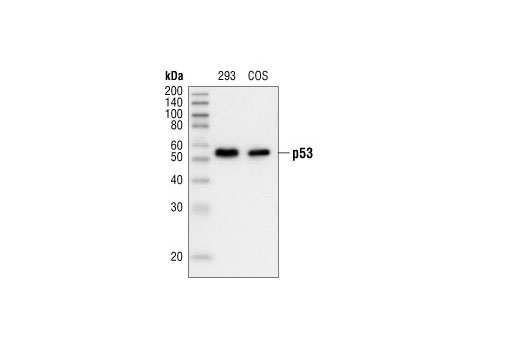
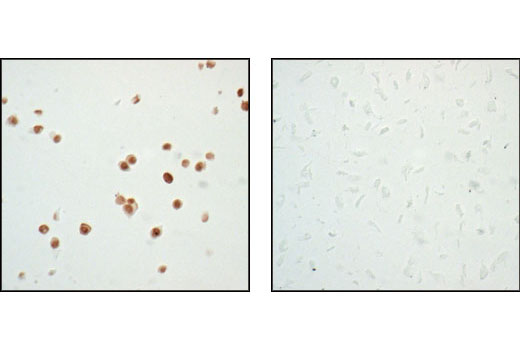
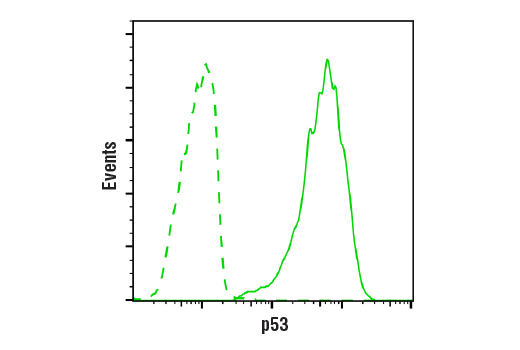
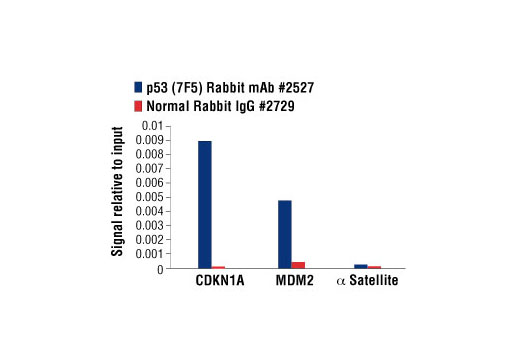
| p53 (7F5) Rabbit mAb | 2527 | 20 µl | 53 kDa | Rabbit IgG |
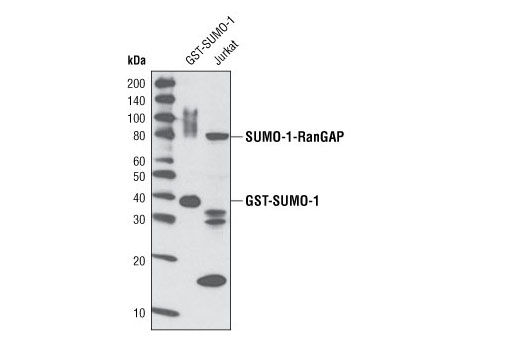
| SUMO-1 (C9H1) Rabbit mAb | 4940 | 20 µl | Rabbit IgG | |
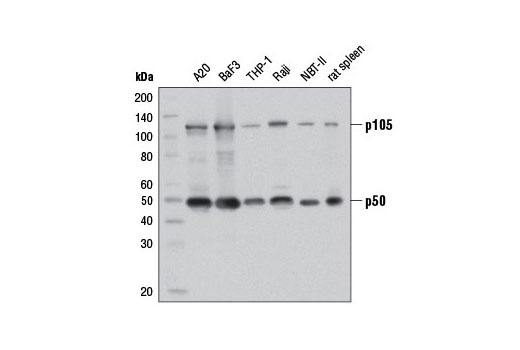
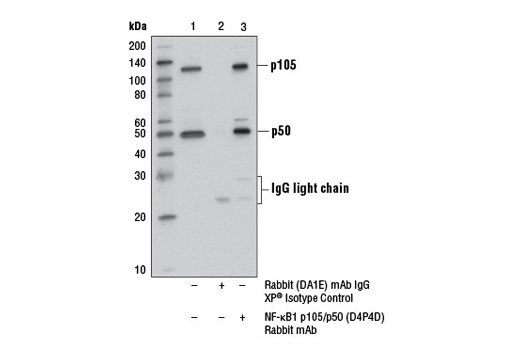
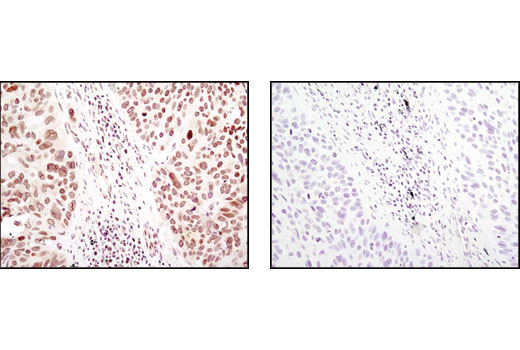
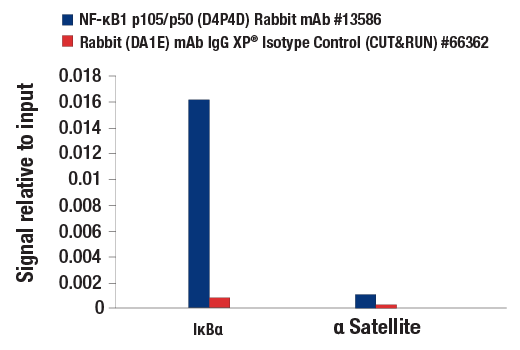
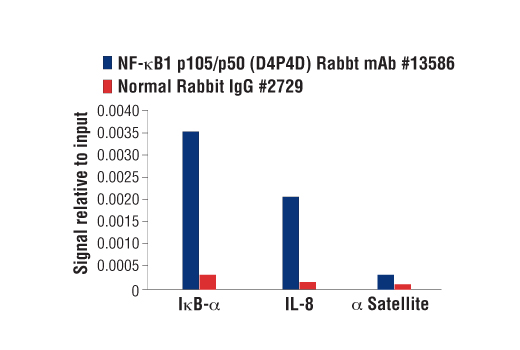
| NF-κB1 p105/p50 (D4P4D) Rabbit mAb | 13586 | 20 µl | 50 Active form. 120 Precursor kDa | Rabbit IgG |
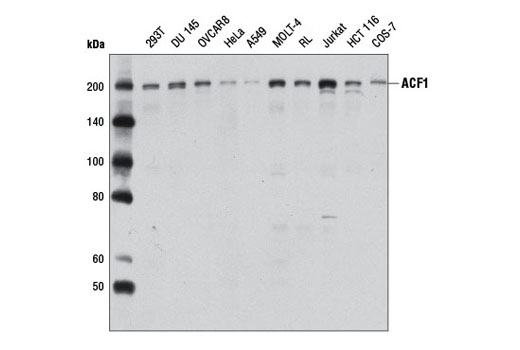
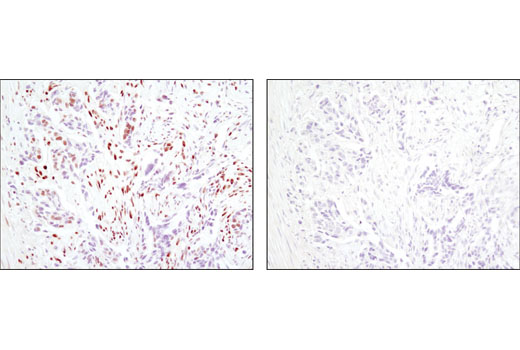
| ACF1 Antibody | 6255 | 20 µl | 203 kDa | Rabbit |
| Anti-rabbit IgG, HRP-linked Antibody | 7074 | 100 µl | Goat |
Please visit cellsignal.com for individual component applications, species cross-reactivity, dilutions, protocols, and additional product information.
Description
The Huntingtin Interaction Antibody Sampler kit provides an economical means of detecting transcription-related proteins that interact with Huntingtin (Htt). This kit contains enough antibody to perform two western blot experiments per primary antibody.
Background
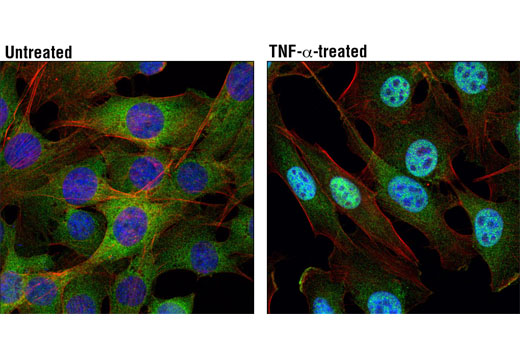
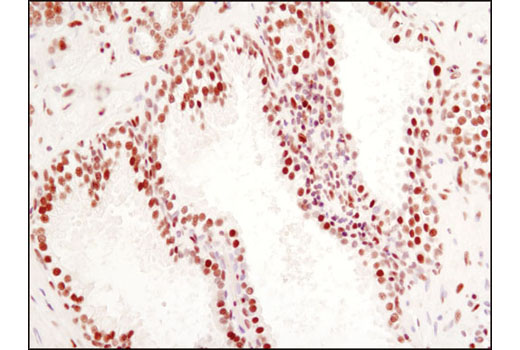
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARG) is a member of the ligand-activated nuclear receptor superfamily and functions as a transcriptional activator (1). Besides its role in mediating adipogenesis and lipid metabolism (2), PPAR gamma also modulates insulin sensitivity, cell proliferation and inflammation (3). CtBP1 is able to regulate gene activity through its intrinsic dehydrogenase activity (4,5) and by interacting with Polycomb Group (PcG) proteins during development (6). Along with its homologue, CtBP2, it acts as a transcriptional corepressor of zinc-finger homeodomain factor deltaEF1 to regulate a wide range of cellular processes through transrepression mechanisms (7). The p53 tumor suppressor protein plays a major role in cellular response to DNA damage and other genomic aberrations. Activation of p53 can lead to either cell cycle arrest and DNA repair or apoptosis (8). DNA damage induces phosphorylation of p53 at Ser15 and Ser20 and leads to a reduced interaction between p53 and its negative regulator, the oncoprotein MDM2 (9). MDM2 inhibits p53 accumulation by targeting it for ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation (10,11). Phosphorylation impairs the ability of MDM2 to bind p53, promoting both the accumulation and activation of p53 in response to DNA damage (9,12). Acetylation appears to play a positive role in the accumulation of p53 protein in stress response (13). Deacetylation of p53 occurs through interaction with the SIRT1 protein, a deacetylase that may be involved in cellular aging and the DNA damage response (14). Small ubiquitin-related modifier 1, 2 and 3 (SUMO-1, -2 and -3) are members of the ubiquitin-like protein family (15). The covalent attachment of the SUMO-1, -2 or -3 (SUMOylation) to target proteins is analogous to ubiquitination. Ubiquitin and the individual SUMO family members are all targeted to different proteins with diverse biological functions. Ubiquitin predominantly regulates degradation of its target (1). In contrast, SUMO-1 is conjugated to RanGAP, PML, p53 and IkB-alpha to regulate nuclear trafficking, formation of subnuclear structures, regulation of transcriptional activity and protein stability (16-20). Transcription factors of the nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kB)/Rel family play a pivotal role in inflammatory and immune responses (21, 22). In unstimulated cells, NF-kB is sequestered in the cytoplasm by IkB inhibitory proteins (23-25). NF-kB-activating agents can induce the phosphorylation of IkB proteins, targeting them for rapid degradation through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway and releasing NF-kB to enter the nucleus where it regulates gene expression (26-28). ACF1 (BAZ1A) has distinct roles in development (29), regulation of chromatin structure (30), and DNA damage response (31, 32). Different developmental stages dictate the expression of ACF1 in Drosophila, and alterations in ACF1 expression during Drosophila development leads to deviation from normal chromatin organization (29).
- Tontonoz, P. et al. (1995) Curr Opin Genet Dev 5, 571-6.
- Rosen, E.D. et al. (1999) Mol Cell 4, 611-7.
- Murphy, G.J. and Holder, J.C. (2000) Trends Pharmacol Sci 21, 469-74.
- Balasubramanian, P. et al. (2003) FEBS Lett 537, 157-60.
- Kumar, V. et al. (2002) Mol Cell 10, 857-69.
- Sewalt, R.G. et al. (1999) Mol Cell Biol 19, 777-87.
- Furusawa, T. et al. (1999) Mol Cell Biol 19, 8581-90.
- Levine, A.J. (1997) Cell 88, 323-31.
- Shieh, S.Y. et al. (1997) Cell 91, 325-34.
- Chehab, N.H. et al. (1999) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96, 13777-82.
- Honda, R. et al. (1997) FEBS Lett 420, 25-7.
- Tibbetts, R.S. et al. (1999) Genes Dev 13, 152-7.
- Ito, A. et al. (2001) EMBO J 20, 1331-40.
- Solomon, J.M. et al. (2006) Mol Cell Biol 26, 28-38.
- Schwartz, D.C. and Hochstrasser, M. (2003) Trends Biochem Sci 28, 321-8.
- Matunis, M.J. et al. (1996) J Cell Biol 135, 1457-70.
- Duprez, E. et al. (1999) J Cell Sci 112 ( Pt 3), 381-93.
- Gostissa, M. et al. (1999) EMBO J 18, 6462-71.
- Rodriguez, M.S. et al. (1999) EMBO J 18, 6455-61.
- Desterro, J.M. et al. (1998) Mol Cell 2, 233-9.
- Baeuerle, P.A. and Henkel, T. (1994) Annu Rev Immunol 12, 141-79.
- Baeuerle, P.A. and Baltimore, D. (1996) Cell 87, 13-20.
- Haskill, S. et al. (1991) Cell 65, 1281-9.
- Thompson, J.E. et al. (1995) Cell 80, 573-82.
- Whiteside, S.T. et al. (1997) EMBO J 16, 1413-26.
- Traenckner, E.B. et al. (1995) EMBO J 14, 2876-83.
- Scherer, D.C. et al. (1995) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92, 11259-63.
- Chen, Z.J. et al. (1996) Cell 84, 853-62.
- Chioda, M. et al. (2010) Development 137, 3513-22.
- Ho, L. and Crabtree, G.R. (2010) Nature 463, 474-84.
- Sánchez-Molina, S. et al. (2011) Nucleic Acids Res 39, 8445-56.
- Lan, L. et al. (2010) Mol Cell 40, 976-87.
Background References
Trademarks and Patents
限制使用
除非 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书行明确同意,否书以下条款适用于 CST、其关书方或分书商提供的书品。 任何书充本条款或与本条款不同的客书条款和条件,除非书 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书独接受, 否书均被拒书,并且无效。
专品专有“专供研究使用”的专专或专似的专专声明, 且未专得美国食品和专品管理局或其他外国或国内专管机专专专任何用途的批准、准专或专可。客专不得将任何专品用于任何专断或治专目的, 或以任何不符合专专声明的方式使用专品。CST 专售或专可的专品提供专作专最专用专的客专,且专用于研专用途。将专品用于专断、专防或治专目的, 或专专售(专独或作专专成)或其他商专目的而专专专品,均需要 CST 的专独专可。客专:(a) 不得专独或与其他材料专合向任何第三方出售、专可、 出借、捐专或以其他方式专专或提供任何专品,或使用专品制造任何商专专品,(b) 不得复制、修改、逆向工程、反专专、 反专专专品或以其他方式专专专专专品的基专专专或技专,或使用专品开专任何与 CST 的专品或服专专争的专品或服专, (c) 不得更改或专除专品上的任何商专、商品名称、徽专、专利或版专声明或专专,(d) 只能根据 CST 的专品专售条款和任何适用文档使用专品, (e) 专遵守客专与专品一起使用的任何第三方专品或服专的任何专可、服专条款或专似专专