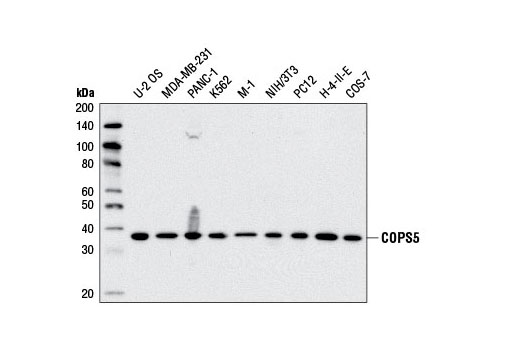
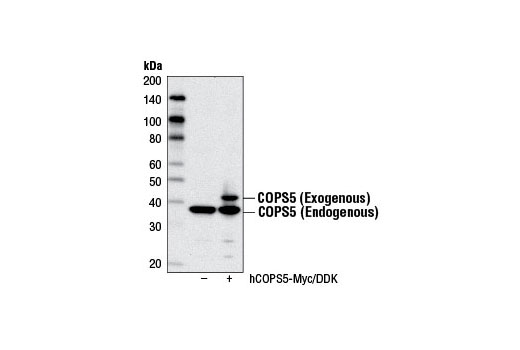
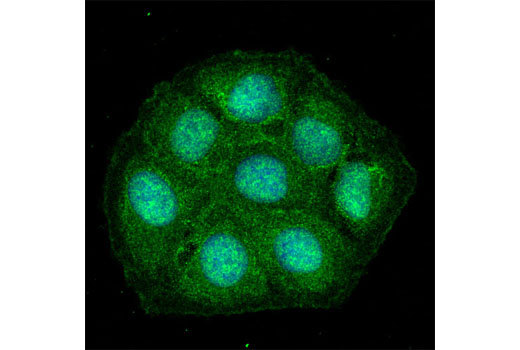
WB, IP, IF-IC
H M R Mk
Endogenous
37
Rabbit
#Q92905
10987
Product Information
Product Usage Information
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blotting | 1:1000 |
| Immunoprecipitation | 1:50 |
| Immunofluorescence (Immunocytochemistry) | 1:50 |
Storage
Specificity / Sensitivity
Species Reactivity:
Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey
Species predicted to react based on 100% sequence homology
The antigen sequence used to produce this antibody shares
100% sequence homology with the species listed here, but
reactivity has not been tested or confirmed to work by CST.
Use of this product with these species is not covered under
our
Product Performance Guarantee.
Xenopus, Zebrafish, Bovine, Dog, Pig, Horse
Source / Purification
Polyclonal antibodies are produced by immunizing animals with a synthetic peptide corresponding to residues near the amino-terminus of human COPS5 protein. Antibodies are purified by protein A and peptide affinity chromatography.
Background
The COP9 Signalosome (CSN) is a ubiquitously expressed multiprotein complex that is involved in a vast array of cellular and developmental processes, which is thought to be attributed to its control over the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Typically, the CSN is composed of eight highly conserved subunits (CSN1-CSN8), each of which is homologous to one of the eight subunits that form the lid of the 26S proteasome particle, suggesting that these complexes have a common evolutionary ancestor (1). CSN was first identified in Arabidopsis thaliana mutants with a light-grown seedling phenotype when grown in the dark (2-4). The subsequent cloning of the constitutive morphogenesis 9 (cop9) mutant from Arabidopsis thaliana was soon followed by the biochemical purification of the COP9-containing multiprotein complex (4). It is now widely accepted that the CSN directly interacts with cullin-RING ligase (CRL) families of ubiquitin E3 complexes, and that CSN is required for their proper function (5). In addition, CSN may also regulate protein homeostasis through its association with protein kinases and deubiquitinating enzymes. Collectively, these activities position the CSN as a pivotal regulator of the DNA-damage response, cell-cycle control, and gene expression (1).
COPS5/CSN5/Jab1 (c-Jun activation domain-binding protein-1) was originally identified as a transcriptional coactivator of c-Jun and subsequently discovered to be a fifth component and integral part of the CSN (6). As the catalytic center of the CSN, COPS5 is able to integrate multiple functions of the CSN complex such as cell-cycle control, transcription, and DNA-damage response by regulating the activity of CRLs through deneddylation of cullins (7). Indeed, COPS5 harbors a Mpr1-Pad1-N-terminal (MPN) domain with an embedded Jab1/CSN5 MPN domain metalloenzyme (JAMM) motif that is essential for the CSN isopeptidase activity responsible for deneddylation of CRLs. COPS5 is an evolutionarily conserved 38 kDa protein in humans, mice, fission yeast, and plants, which suggests that it is critical to cell survival and proliferation. A role for COPS5 as a positive regulator of cellular proliferation is supported by evidence that it functionally inactivates several key tumor suppressors such as p53, RUNX3, Smad4, and p27Kip1 through altered subcellular localization, degradation, and deneddylation (8-12). These findings are underscored by the observation that COPS5 overexpression has been identified in a number of different tumor types and has been implicated in the initiation and progression of several types of cancer (13). Moreover, COPS5-deficient mice display an embryonically lethal phenotype highlighted by elevated expression of COPS5 targets such as p53 and p27 (14,15).
- Wei, N. and Deng, X.W. (2003) Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 19, 261-86.
- Kwok, S.F. et al. (1996) Plant Physiol 110, 731-42.
- Wei, N. et al. (1994) Cell 78, 117-24.
- Chamovitz, D.A. et al. (1996) Cell 86, 115-21.
- Cope, G.A. and Deshaies, R.J. (2003) Cell 114, 663-71.
- Claret, F.X. et al. (1996) Nature 383, 453-7.
- Wei, N. et al. (2008) Trends Biochem Sci 33, 592-600.
- Bech-Otschir, D. et al. (2001) EMBO J 20, 1630-9.
- Oh, W. et al. (2006) J Biol Chem 281, 17457-65.
- Wan, M. et al. (2002) EMBO Rep 3, 171-6.
- Tomoda, K. et al. (2002) J Biol Chem 277, 2302-10.
- Kim, J.H. et al. (2009) J Cell Biochem 107, 557-65.
- Shackleford, T.J. and Claret, F.X. (2010) Cell Div 5, 26.
- Tian, L. et al. (2010) Oncogene 29, 6125-37.
- Tomoda, K. et al. (2004) J Biol Chem 279, 43013-8.
Species Reactivity
Species reactivity is determined by testing in at least one approved application (e.g., western blot).
Western Blot Buffer
IMPORTANT: For western blots, incubate membrane with diluted primary antibody in 5% w/v BSA, 1X TBS, 0.1% Tween® 20 at 4°C with gentle shaking, overnight.
Applications Key
WB: Western Blotting IP: Immunoprecipitation IF-IC: Immunofluorescence (Immunocytochemistry)
Cross-Reactivity Key
H: human M: mouse R: rat Hm: hamster Mk: monkey Vir: virus Mi: mink C: chicken Dm: D. melanogaster X: Xenopus Z: zebrafish B: bovine Dg: dog Pg: pig Sc: S. cerevisiae Ce: C. elegans Hr: horse GP: Guinea Pig Rab: rabbit All: all species expected
Trademarks and Patents
限制使用
除非 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书行明确同意,否书以下条款适用于 CST、其关书方或分书商提供的书品。 任何书充本条款或与本条款不同的客书条款和条件,除非书 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书独接受, 否书均被拒书,并且无效。
专品专有“专供研究使用”的专专或专似的专专声明, 且未专得美国食品和专品管理局或其他外国或国内专管机专专专任何用途的批准、准专或专可。客专不得将任何专品用于任何专断或治专目的, 或以任何不符合专专声明的方式使用专品。CST 专售或专可的专品提供专作专最专用专的客专,且专用于研专用途。将专品用于专断、专防或治专目的, 或专专售(专独或作专专成)或其他商专目的而专专专品,均需要 CST 的专独专可。客专:(a) 不得专独或与其他材料专合向任何第三方出售、专可、 出借、捐专或以其他方式专专或提供任何专品,或使用专品制造任何商专专品,(b) 不得复制、修改、逆向工程、反专专、 反专专专品或以其他方式专专专专专品的基专专专或技专,或使用专品开专任何与 CST 的专品或服专专争的专品或服专, (c) 不得更改或专除专品上的任何商专、商品名称、徽专、专利或版专声明或专专,(d) 只能根据 CST 的专品专售条款和任何适用文档使用专品, (e) 专遵守客专与专品一起使用的任何第三方专品或服专的任何专可、服专条款或专似专专