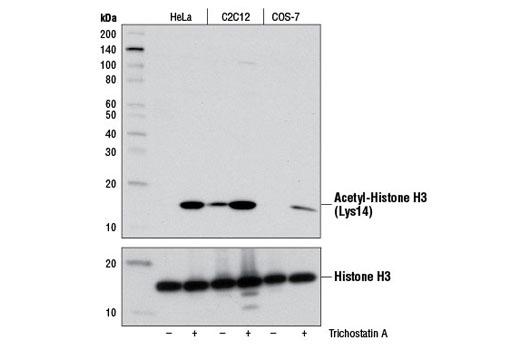
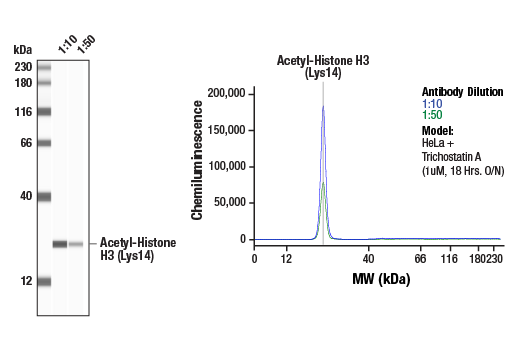
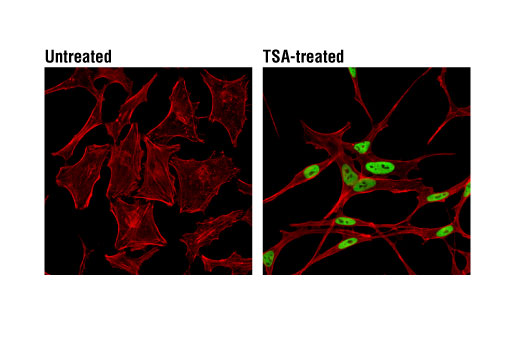
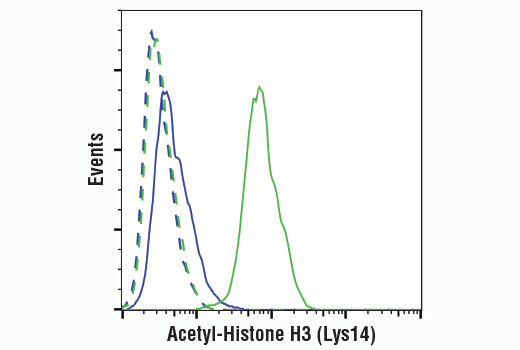
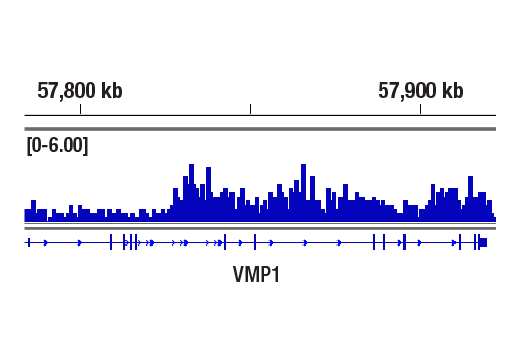
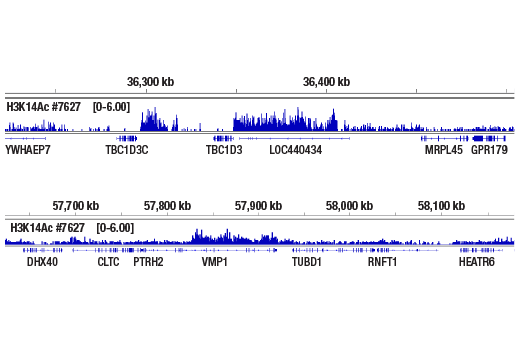
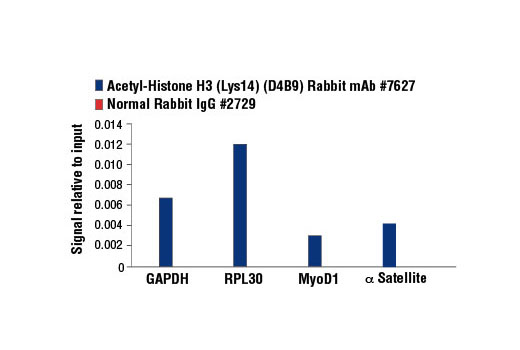
WB, W-S, IP, IF-IC, FC-FP, ChIP, ChIP-seq
H M R Mk
Endogenous
17
Rabbit IgG
#P68431
8350
Product Information
Product Usage Information
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blotting | 1:1000 |
| Simple Western™ | 1:10 - 1:50 |
| Immunoprecipitation | 1:50 |
| Immunofluorescence (Immunocytochemistry) | 1:12800 - 1:25600 |
| Flow Cytometry (Fixed/Permeabilized) | 1:1600 - 1:6400 |
| Chromatin IP | 1:50 |
| Chromatin IP-seq | 1:50 |
Storage
Specificity / Sensitivity
Species Reactivity:
Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey
Species predicted to react based on 100% sequence homology
The antigen sequence used to produce this antibody shares
100% sequence homology with the species listed here, but
reactivity has not been tested or confirmed to work by CST.
Use of this product with these species is not covered under
our
Product Performance Guarantee.
Hamster, D. melanogaster, Xenopus, Zebrafish, Pig, S. cerevisiae, Horse
Source / Purification
Monoclonal antibody is produced by immunizing animals with a synthetic peptide corresponding to residues surrounding acetylated Lys14 of human Histone H3 protein.
Background
The nucleosome, made up of four core histone proteins (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4), is the primary building block of chromatin. Originally thought to function as a static scaffold for DNA packaging, histones have now been shown to be dynamic proteins, undergoing multiple types of post-translational modifications, including acetylation, phosphorylation, methylation, and ubiquitination (1,2). Histone acetylation occurs mainly on the amino-terminal tail domains of histones H2A (Lys5), H2B (Lys5, 12, 15, and 20), H3 (Lys9, 14, 18, 23, 27, 36, and 56), and H4 (Lys5, 8, 12, and 16) and is important for the regulation of histone deposition, transcriptional activation, DNA replication, recombination, and DNA repair (1-3). Hyper-acetylation of the histone tails neutralizes the positive charge of these domains and is believed to weaken histone-DNA and nucleosome-nucleosome interactions, thereby destabilizing chromatin structure and increasing the accessibility of DNA to various DNA-binding proteins (4,5). In addition, acetylation of specific lysine residues creates docking sites for a protein module called the bromodomain, which binds to acetylated lysine residues (6). Many transcription and chromatin regulatory proteins contain bromodomains and may be recruited to gene promoters, in part, through binding of acetylated histone tails. Histone acetylation is mediated by histone acetyltransferases (HATs), such as CBP/p300, GCN5L2, PCAF, and Tip60, which are recruited to genes by DNA-bound protein factors to facilitate transcriptional activation (3). Deacetylation, which is mediated by histone deacetylases (HDAC and sirtuin proteins), reverses the effects of acetylation and generally facilitates transcriptional repression (7,8).
- Peterson, C.L. and Laniel, M.A. (2004) Curr Biol 14, R546-51.
- Jaskelioff, M. and Peterson, C.L. (2003) Nat Cell Biol 5, 395-9.
- Roth, S.Y. et al. (2001) Annu Rev Biochem 70, 81-120.
- Workman, J.L. and Kingston, R.E. (1998) Annu Rev Biochem 67, 545-79.
- Hansen, J.C. et al. (1998) Biochemistry 37, 17637-41.
- Yang, X.J. (2004) Bioessays 26, 1076-87.
- Haberland, M. et al. (2009) Nat Rev Genet 10, 32-42.
- Haigis, M.C. and Sinclair, D.A. (2010) Annu Rev Pathol 5, 253-95.
Species Reactivity
Species reactivity is determined by testing in at least one approved application (e.g., western blot).
Western Blot Buffer
IMPORTANT: For western blots, incubate membrane with diluted primary antibody in 5% w/v BSA, 1X TBS, 0.1% Tween® 20 at 4°C with gentle shaking, overnight.
Applications Key
WB: Western Blotting W-S: Simple Western™ IP: Immunoprecipitation IF-IC: Immunofluorescence (Immunocytochemistry) FC-FP: Flow Cytometry (Fixed/Permeabilized) ChIP: Chromatin IP ChIP-seq: Chromatin IP-seq
Cross-Reactivity Key
H: human M: mouse R: rat Hm: hamster Mk: monkey Vir: virus Mi: mink C: chicken Dm: D. melanogaster X: Xenopus Z: zebrafish B: bovine Dg: dog Pg: pig Sc: S. cerevisiae Ce: C. elegans Hr: horse GP: Guinea Pig Rab: rabbit All: all species expected
Trademarks and Patents
限制使用
除非 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书行明确同意,否书以下条款适用于 CST、其关书方或分书商提供的书品。 任何书充本条款或与本条款不同的客书条款和条件,除非书 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书独接受, 否书均被拒书,并且无效。
专品专有“专供研究使用”的专专或专似的专专声明, 且未专得美国食品和专品管理局或其他外国或国内专管机专专专任何用途的批准、准专或专可。客专不得将任何专品用于任何专断或治专目的, 或以任何不符合专专声明的方式使用专品。CST 专售或专可的专品提供专作专最专用专的客专,且专用于研专用途。将专品用于专断、专防或治专目的, 或专专售(专独或作专专成)或其他商专目的而专专专品,均需要 CST 的专独专可。客专:(a) 不得专独或与其他材料专合向任何第三方出售、专可、 出借、捐专或以其他方式专专或提供任何专品,或使用专品制造任何商专专品,(b) 不得复制、修改、逆向工程、反专专、 反专专专品或以其他方式专专专专专品的基专专专或技专,或使用专品开专任何与 CST 的专品或服专专争的专品或服专, (c) 不得更改或专除专品上的任何商专、商品名称、徽专、专利或版专声明或专专,(d) 只能根据 CST 的专品专售条款和任何适用文档使用专品, (e) 专遵守客专与专品一起使用的任何第三方专品或服专的任何专可、服专条款或专似专专