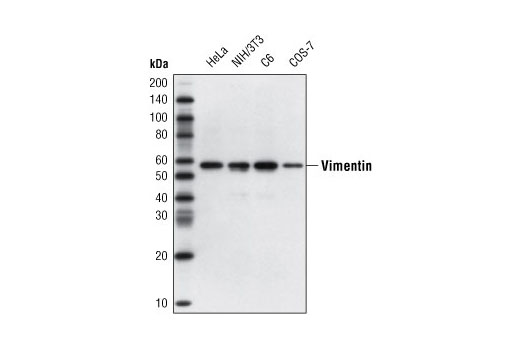
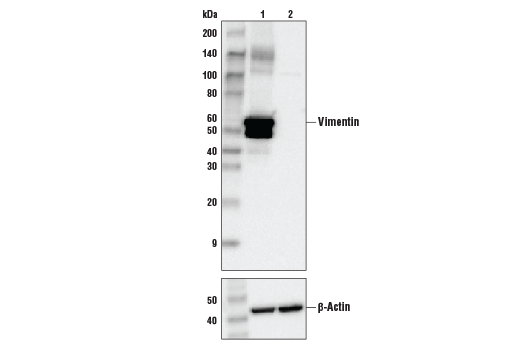
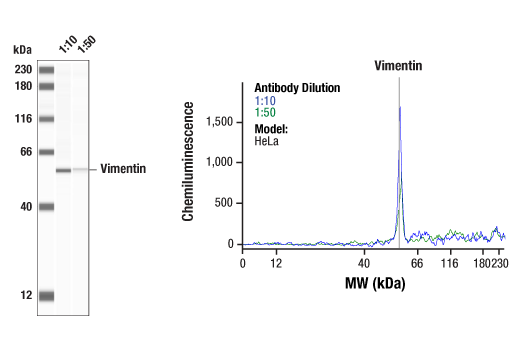
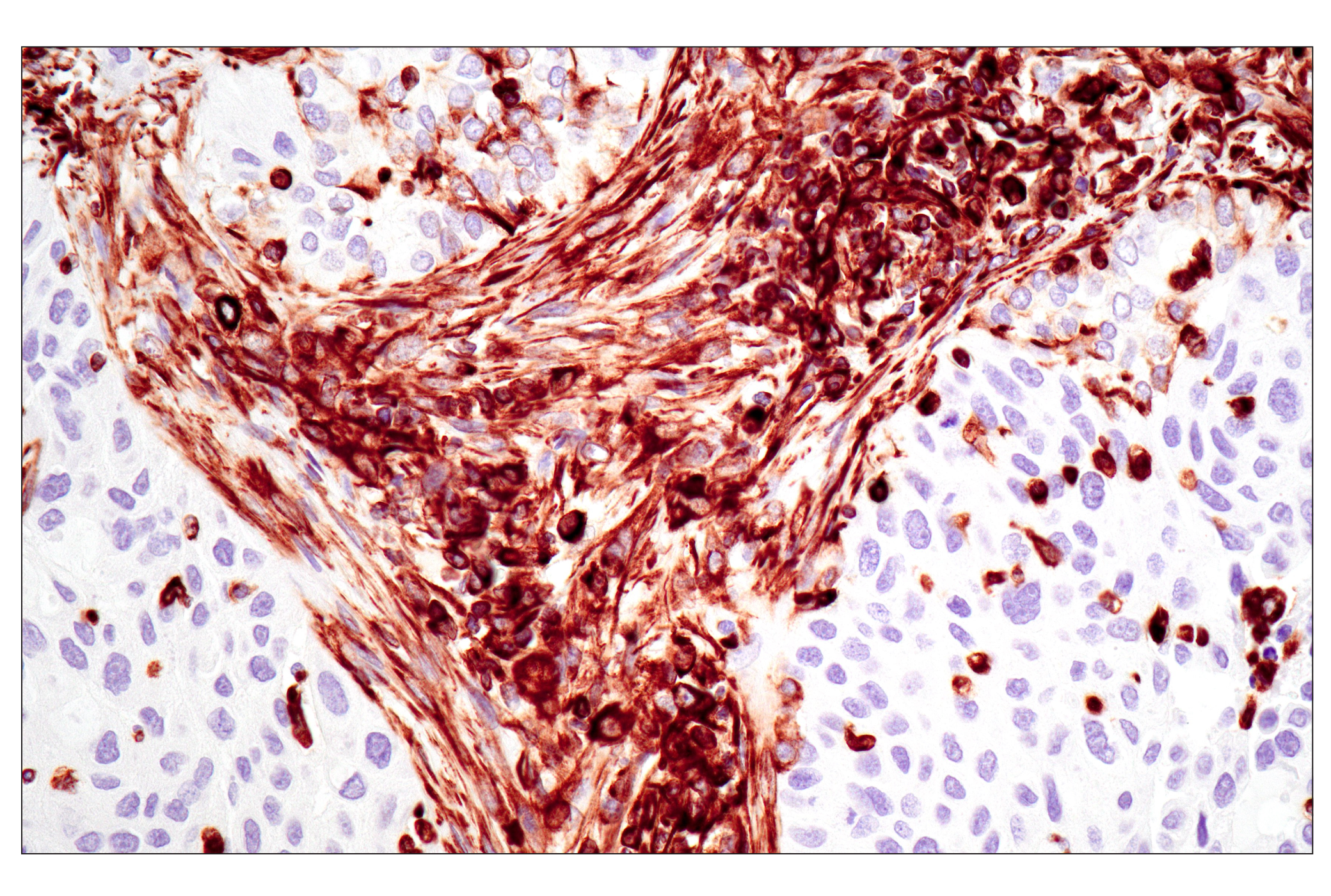
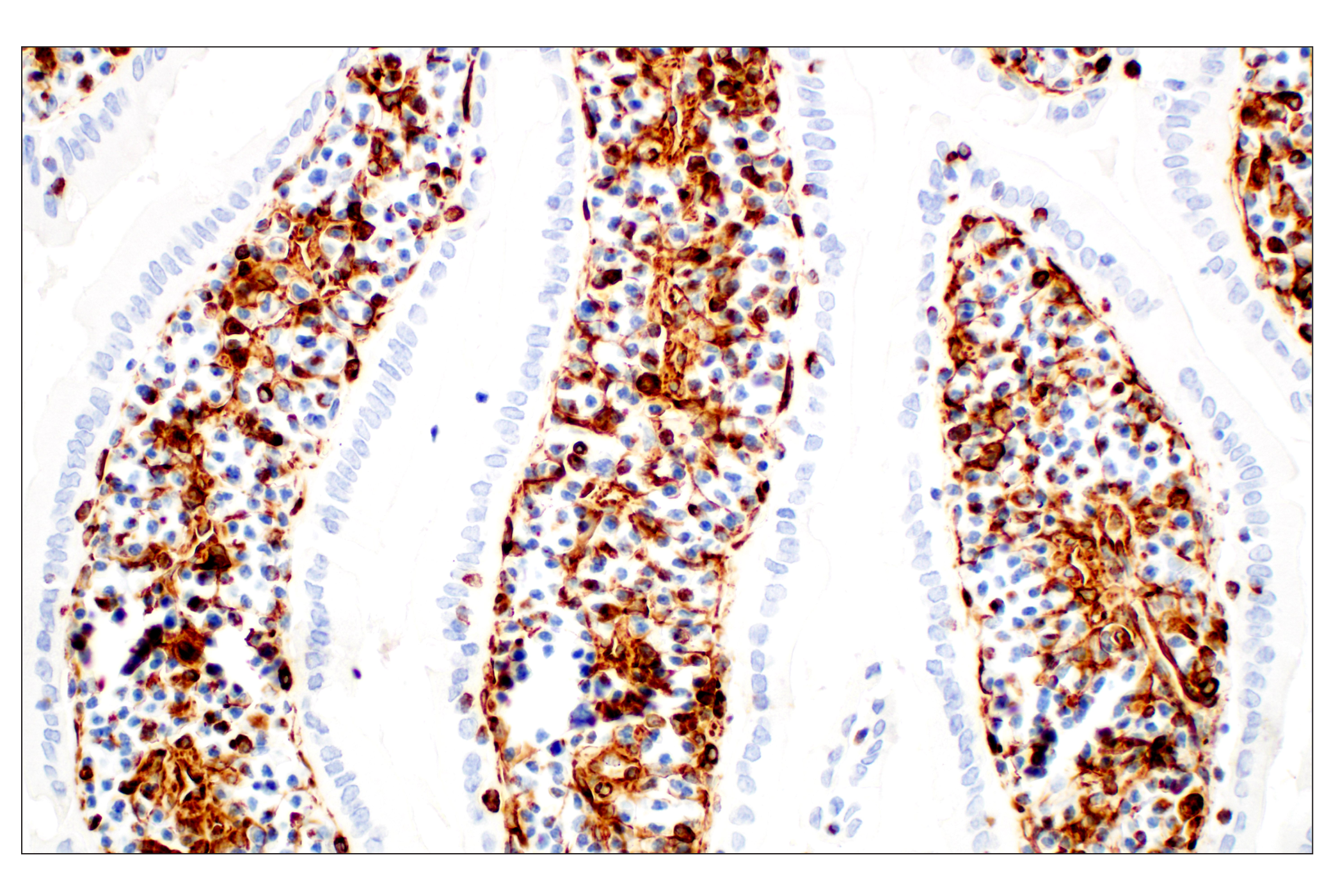
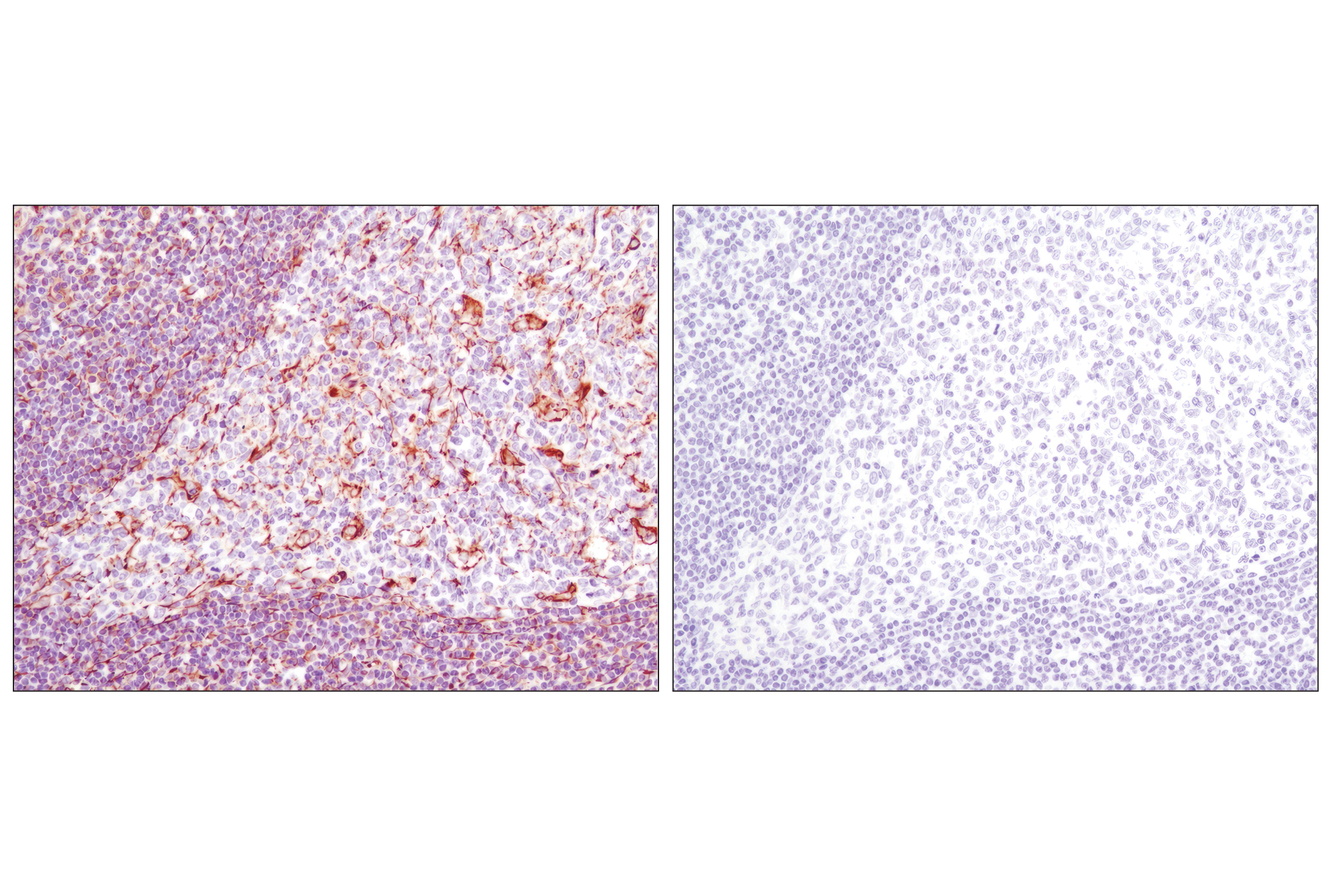
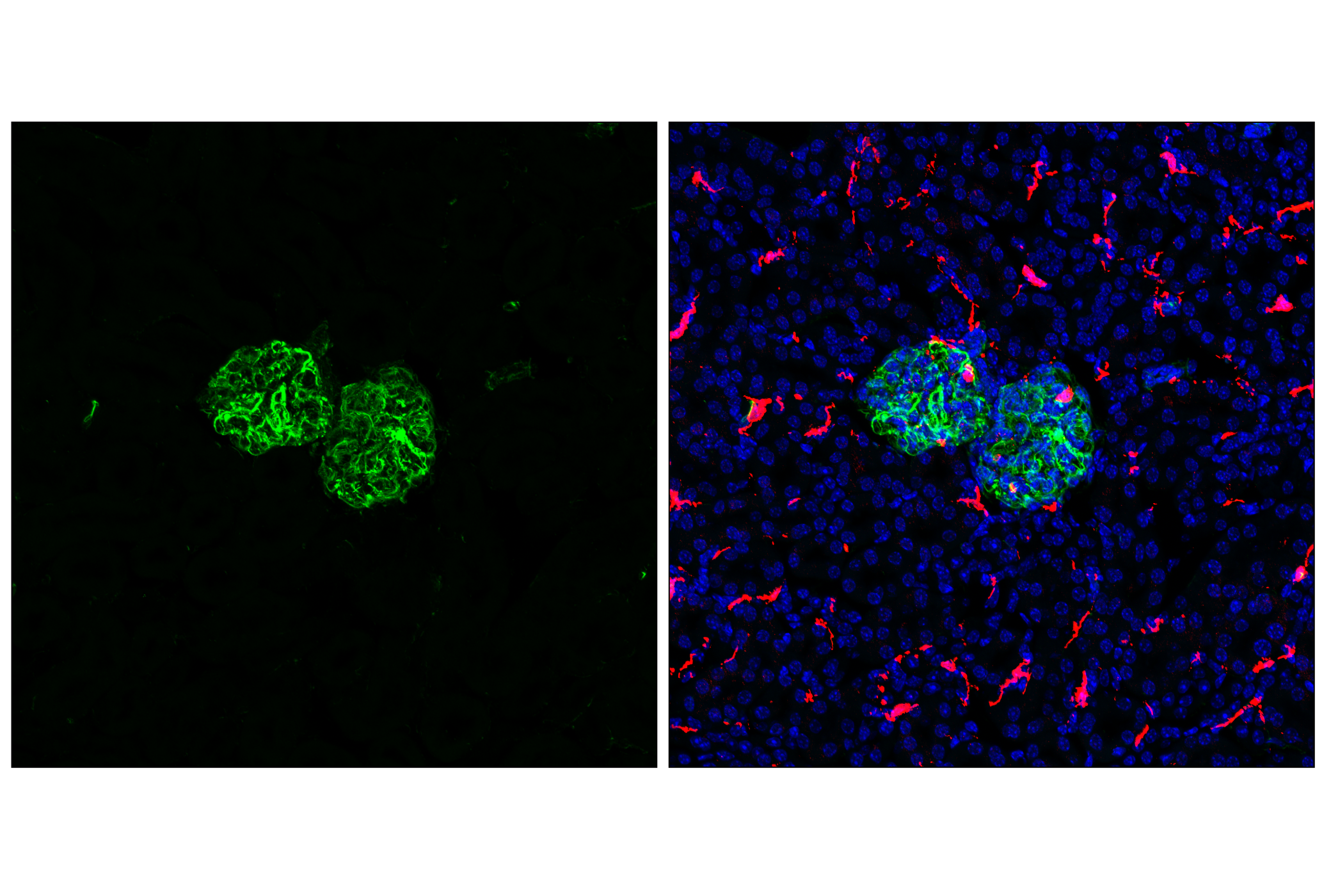
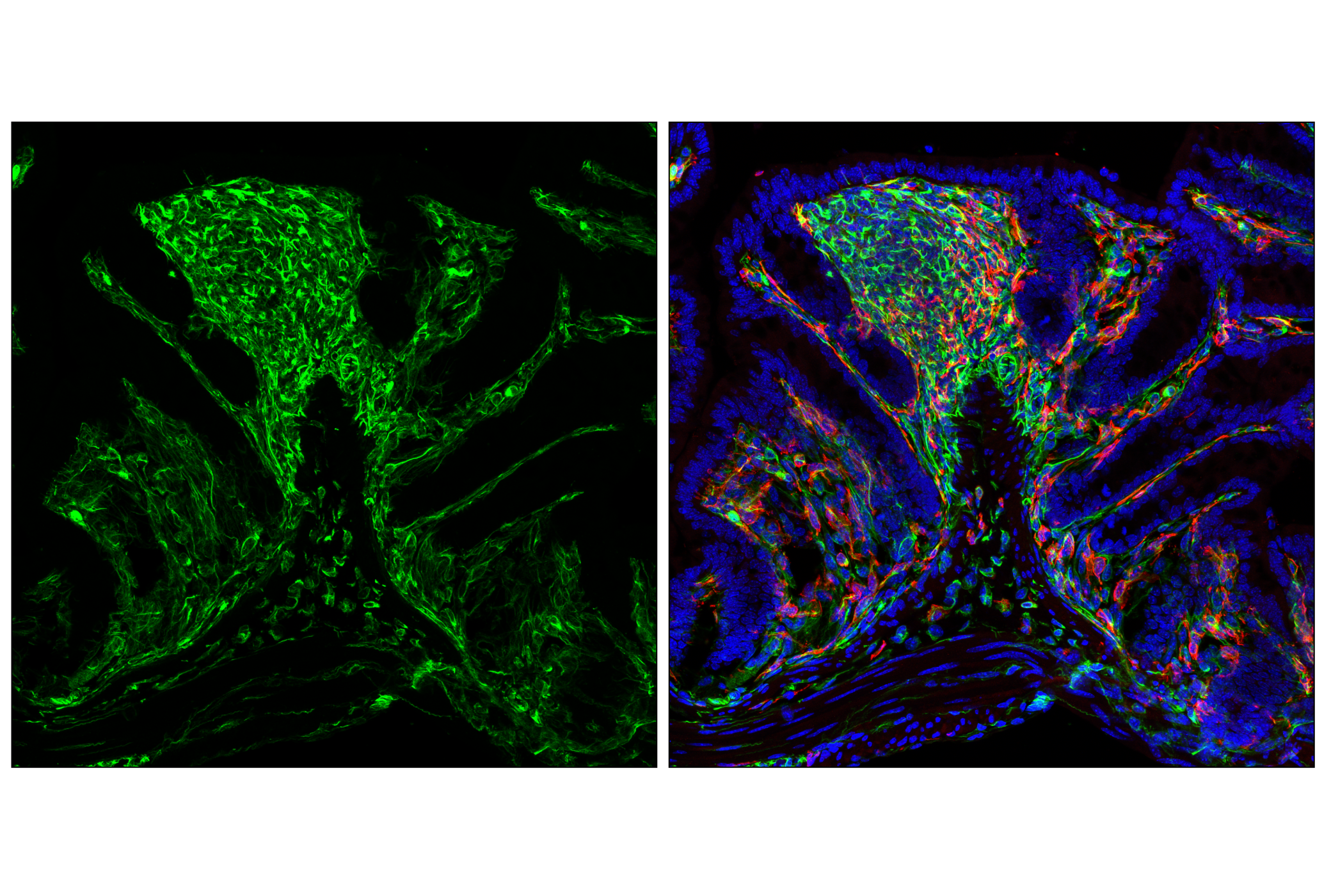
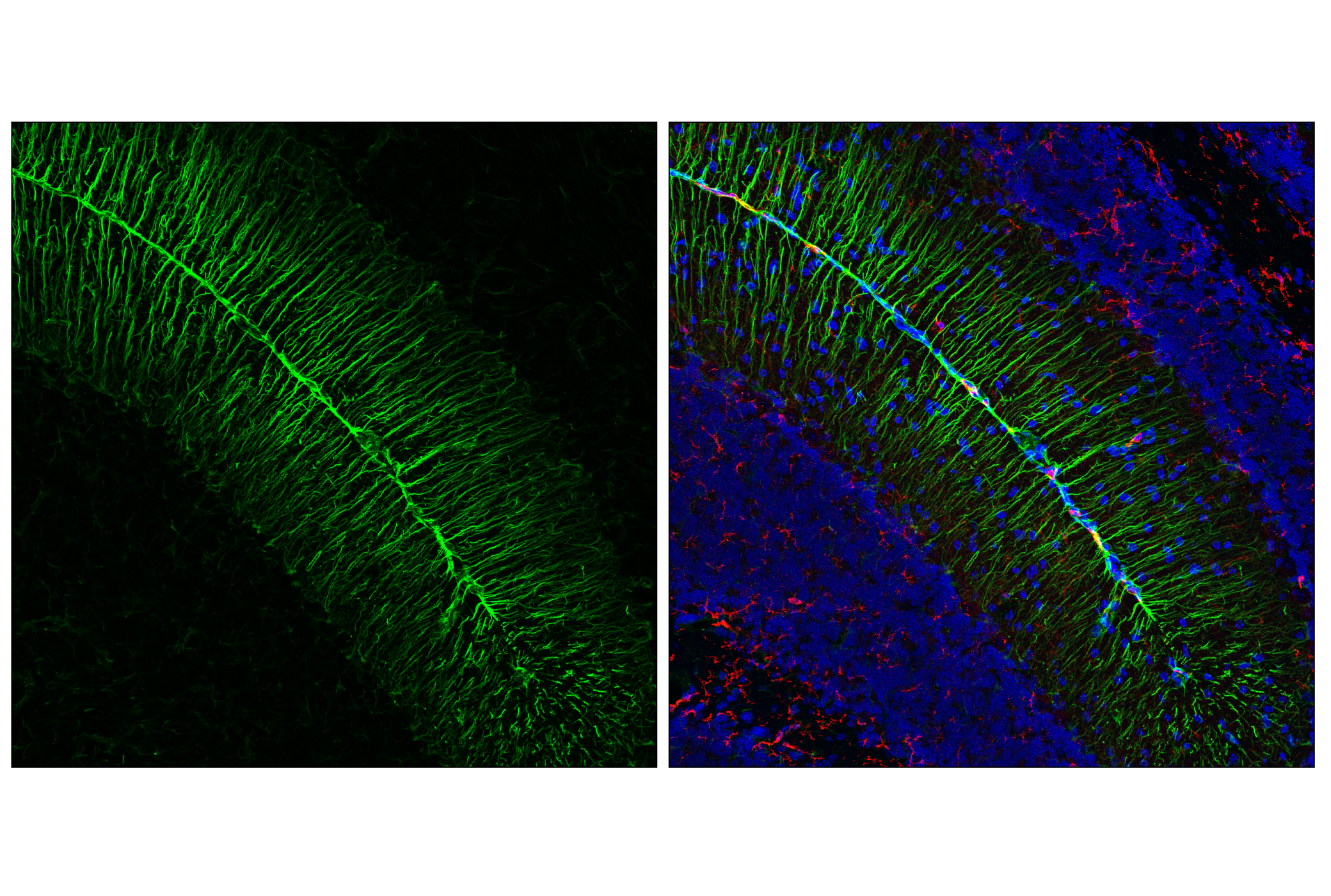
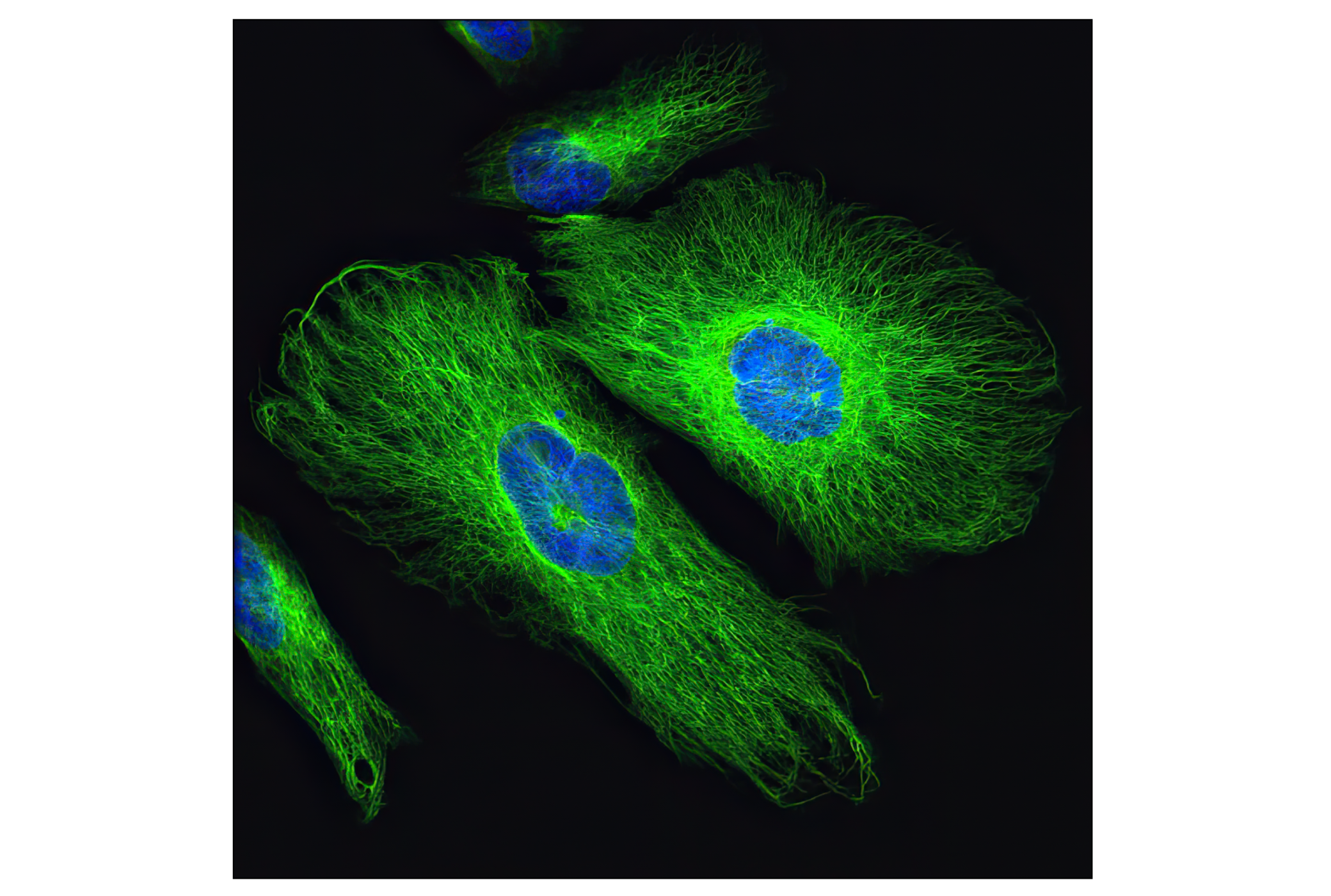
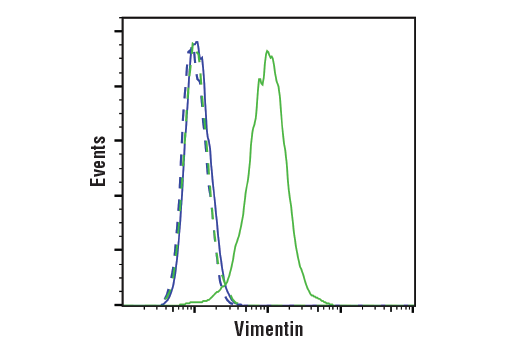
WB, W-S, IHC-Bond, IHC-P, IF-F, IF-IC, FC-FP
H M R Hm Mk
Endogenous
57
Rabbit IgG
#P08670
7431
Product Information
Product Usage Information
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blotting | 1:1000 |
| Simple Western™ | 1:10 - 1:50 |
| IHC Leica Bond | 1:200 - 1:800 |
| Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin) | 1:100 - 1:400 |
| Immunofluorescence (Frozen) | 1:50 - 1:100 |
| Immunofluorescence (Immunocytochemistry) | 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Flow Cytometry (Fixed/Permeabilized) | 1:50 - 1:200 |
Storage
For a carrier free (BSA and azide free) version of this product see product #46173.
Specificity / Sensitivity
Species Reactivity:
Human, Mouse, Rat, Hamster, Monkey
Source / Purification
Monoclonal antibody is produced by immunizing animals with a synthetic peptide corresponding to residues surrounding Arg45 of human vimentin protein.
Background
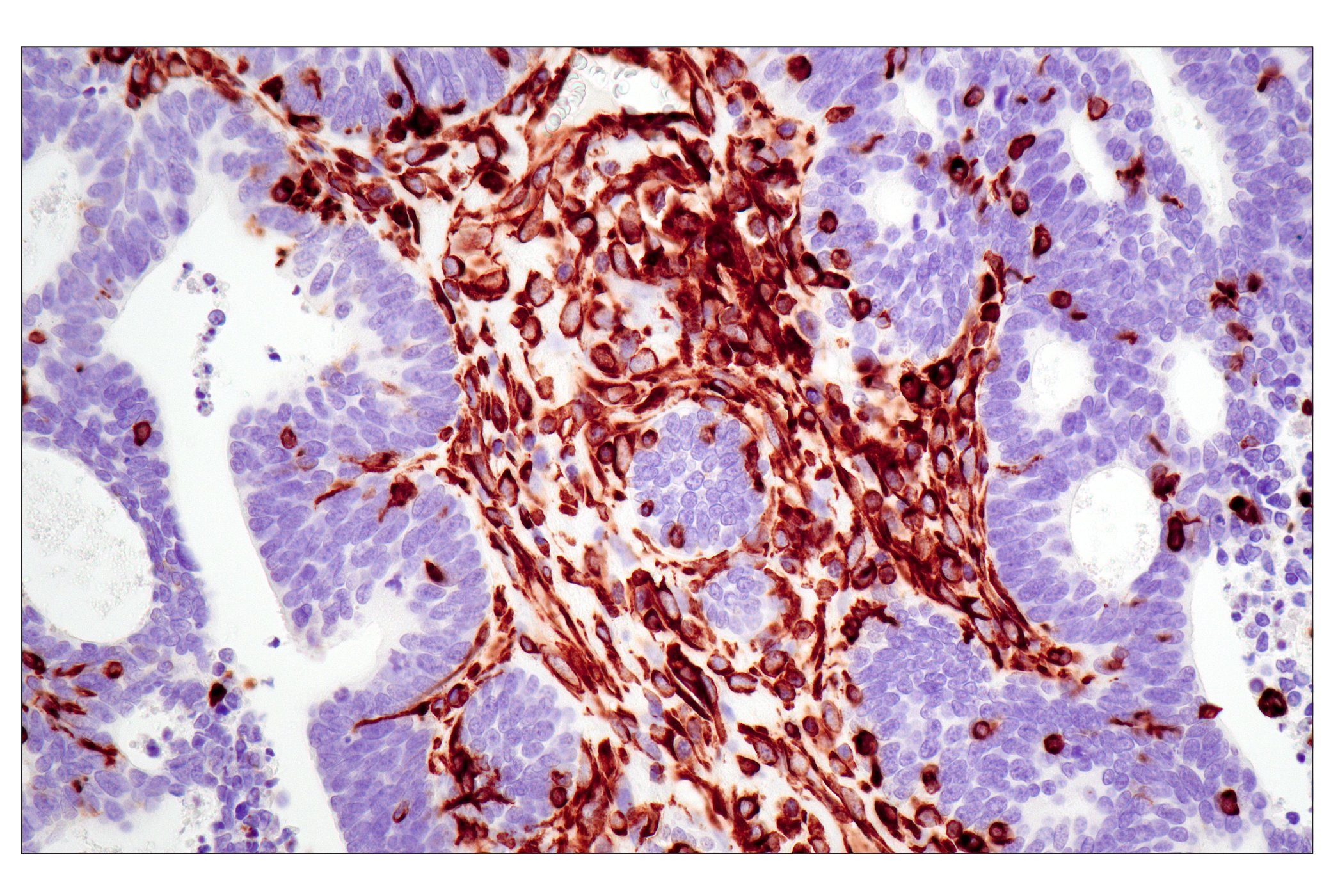
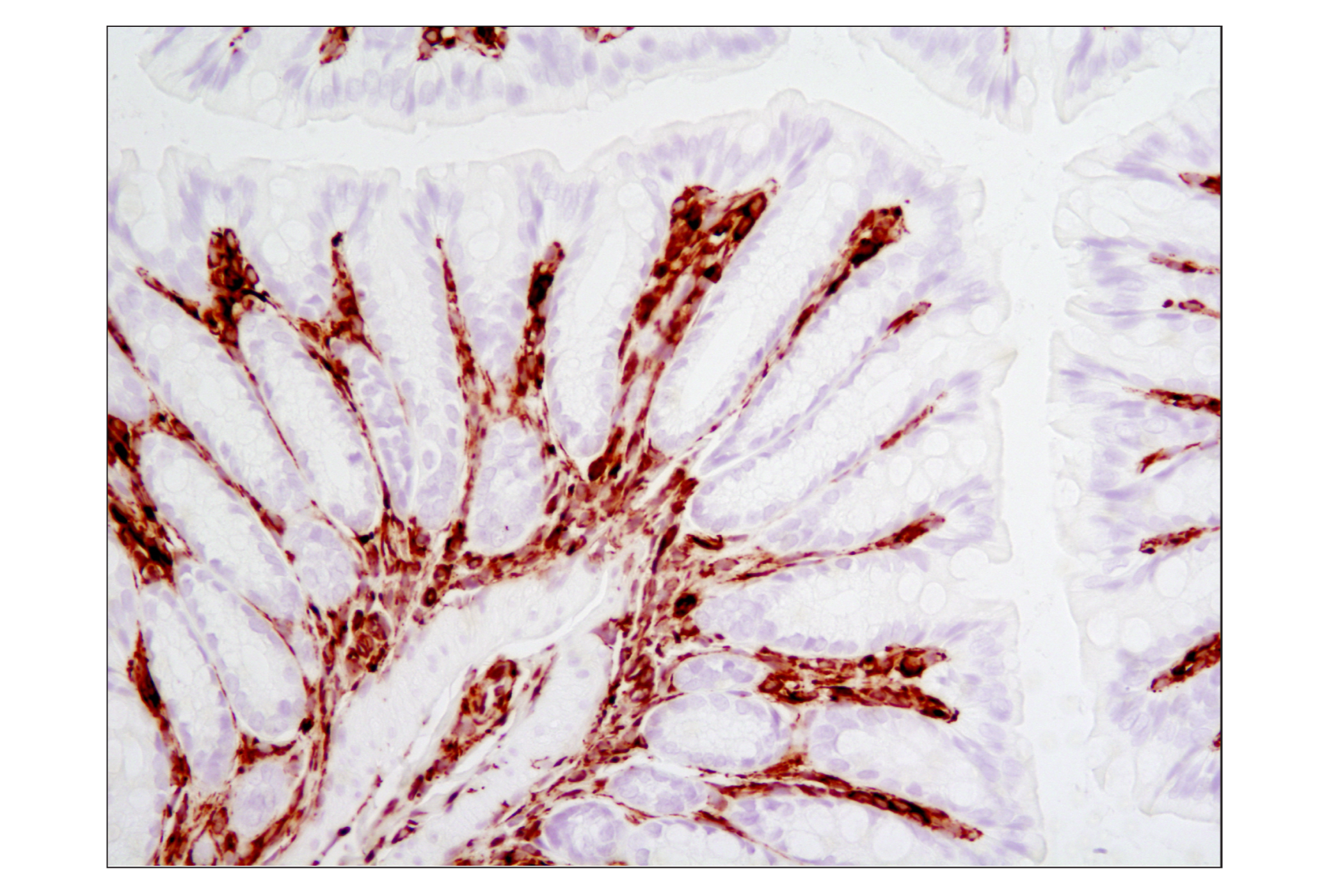
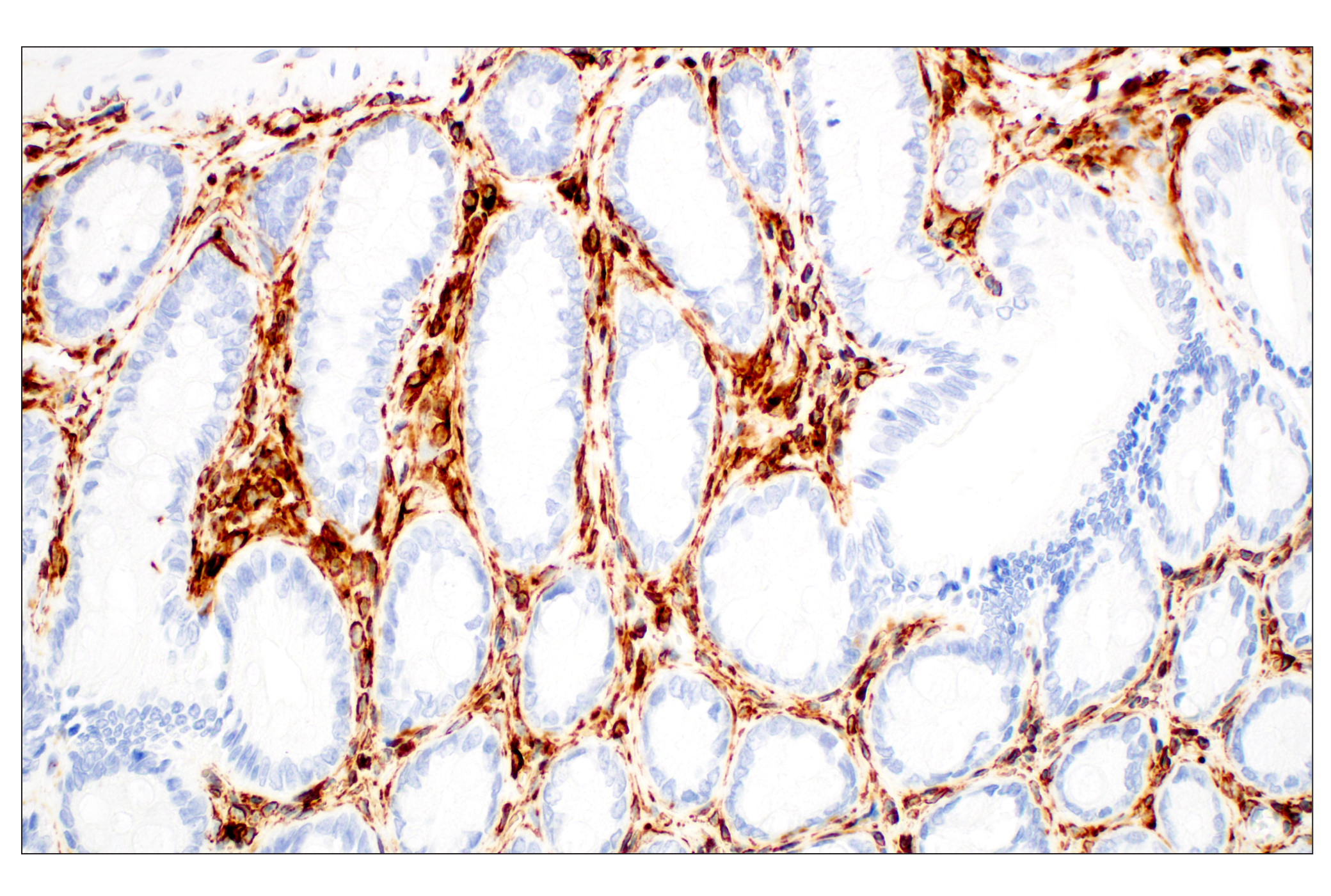
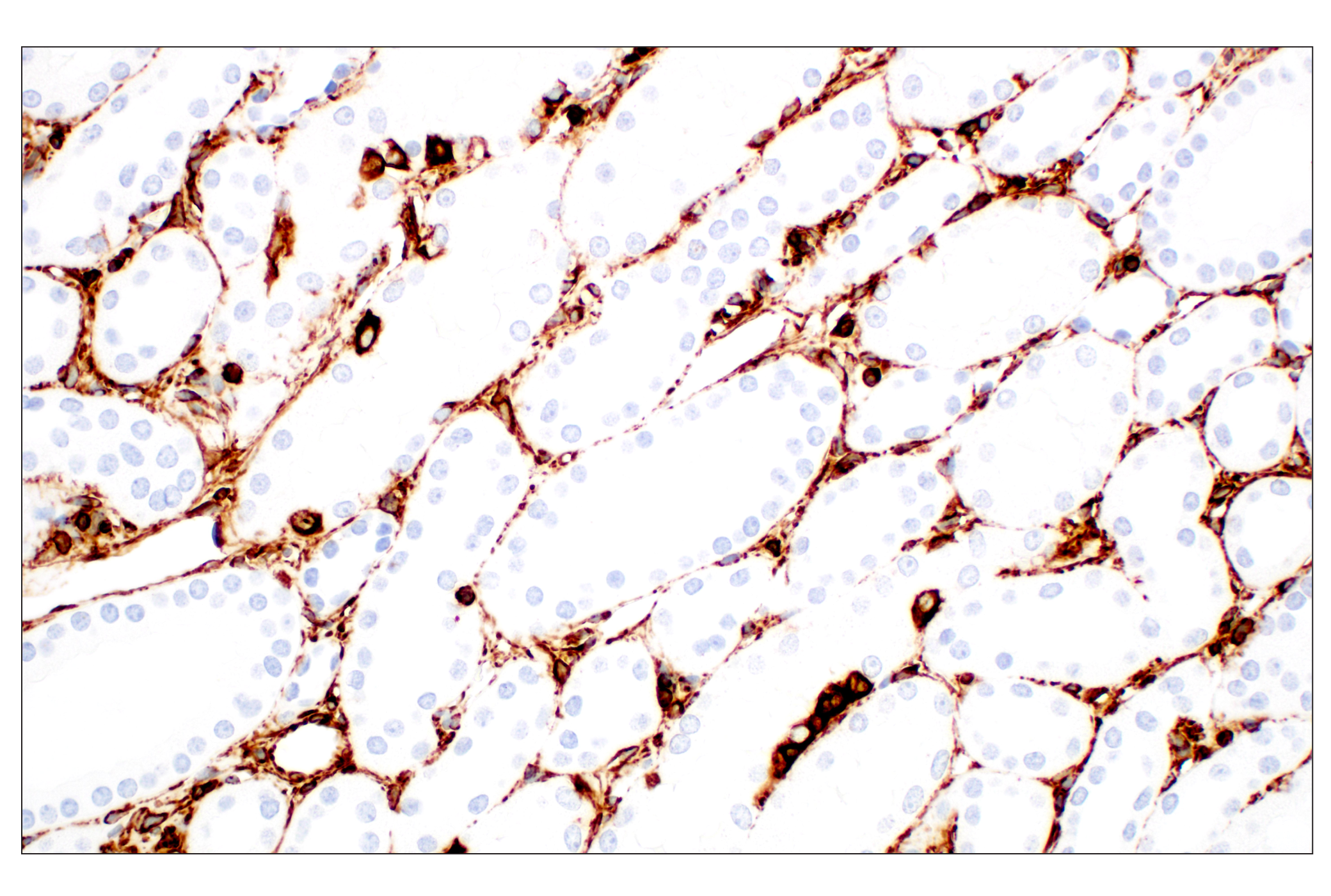
The cytoskeleton consists of three types of cytosolic fibers: microfilaments (actin filaments), intermediate filaments, and microtubules. Major types of intermediate filaments are distinguished by their cell-specific expression: cytokeratins (epithelial cells), glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) (glial cells), desmin (skeletal, visceral, and certain vascular smooth muscle cells), vimentin (mesenchyme origin), and neurofilaments (neurons). GFAP and vimentin form intermediate filaments in astroglial cells and modulate their motility and shape (1). In particular, vimentin filaments are present at early developmental stages, while GFAP filaments are characteristic of differentiated and mature brain astrocytes. Thus, GFAP is commonly used as a marker for intracranial and intraspinal tumors arising from astrocytes (2). Research studies have shown that vimentin is present in sarcomas, but not carcinomas, and its expression is examined in conjunction with that of other markers to distinguish between the two (3). Vimentin's dynamic structural changes and spatial re-organization in response to extracellular stimuli help to coordinate various signaling pathways (4). Phosphorylation of vimentin at Ser56 in smooth muscle cells regulates the structural arrangement of vimentin filaments in response to serotonin (5,6). Remodeling of vimentin and other intermediate filaments is important during lymphocyte adhesion and migration through the endothelium (7).
During mitosis, CDK1 phosphorylates vimentin at Ser56. This phosphorylation provides a PLK binding site for vimentin-PLK interaction. PLK further phosphorylates vimentin at Ser83, which might serve as a memory phosphorylation site and play a regulatory role in vimentin filament disassembly (8,9). Additionally, studies using various soft-tissue sarcoma cells have shown that phosphorylation of vimentin at Ser39 by Akt1 enhances cell migration and survival, suggesting that vimentin could be a potential target for soft-tissue sarcoma targeted therapy (10,11).
- Eng, L.F. et al. (2000) Neurochem Res 25, 1439-51.
- Goebel, H.H. et al. (1987) Acta Histochem Suppl 34, 81-93.
- Leader, M. et al. (1987) Histopathology 11, 63-72.
- Helfand, B.T. et al. (2004) J Cell Sci 117, 133-41.
- Tang, D.D. et al. (2005) Biochem J 388, 773-83.
- Fomina, I.G. et al. (1990) Klin Med (Mosk) 68, 125-7.
- Nieminen, M. et al. (2006) Nat Cell Biol 8, 156-62.
- Yamaguchi, T. et al. (2005) J Cell Biol 171, 431-6.
- Oguri, T. et al. (2006) Genes Cells 11, 531-40.
- Zhu, Q.S. et al. (2011) Oncogene 30, 457-70.
- Xue, G. and Hemmings, B.A. (2013) J Natl Cancer Inst 105, 393-404.
Species Reactivity
Species reactivity is determined by testing in at least one approved application (e.g., western blot).
Western Blot Buffer
IMPORTANT: For western blots, incubate membrane with diluted primary antibody in 5% w/v BSA, 1X TBS, 0.1% Tween® 20 at 4°C with gentle shaking, overnight.
Applications Key
WB: Western Blotting W-S: Simple Western™ IHC-Bond: IHC Leica Bond IHC-P: Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin) IF-F: Immunofluorescence (Frozen) IF-IC: Immunofluorescence (Immunocytochemistry) FC-FP: Flow Cytometry (Fixed/Permeabilized)
Cross-Reactivity Key
H: human M: mouse R: rat Hm: hamster Mk: monkey Vir: virus Mi: mink C: chicken Dm: D. melanogaster X: Xenopus Z: zebrafish B: bovine Dg: dog Pg: pig Sc: S. cerevisiae Ce: C. elegans Hr: horse GP: Guinea Pig Rab: rabbit All: all species expected
Trademarks and Patents
限制使用
除非 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书行明确同意,否书以下条款适用于 CST、其关书方或分书商提供的书品。 任何书充本条款或与本条款不同的客书条款和条件,除非书 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书独接受, 否书均被拒书,并且无效。
专品专有“专供研究使用”的专专或专似的专专声明, 且未专得美国食品和专品管理局或其他外国或国内专管机专专专任何用途的批准、准专或专可。客专不得将任何专品用于任何专断或治专目的, 或以任何不符合专专声明的方式使用专品。CST 专售或专可的专品提供专作专最专用专的客专,且专用于研专用途。将专品用于专断、专防或治专目的, 或专专售(专独或作专专成)或其他商专目的而专专专品,均需要 CST 的专独专可。客专:(a) 不得专独或与其他材料专合向任何第三方出售、专可、 出借、捐专或以其他方式专专或提供任何专品,或使用专品制造任何商专专品,(b) 不得复制、修改、逆向工程、反专专、 反专专专品或以其他方式专专专专专品的基专专专或技专,或使用专品开专任何与 CST 的专品或服专专争的专品或服专, (c) 不得更改或专除专品上的任何商专、商品名称、徽专、专利或版专声明或专专,(d) 只能根据 CST 的专品专售条款和任何适用文档使用专品, (e) 专遵守客专与专品一起使用的任何第三方专品或服专的任何专可、服专条款或专似专专