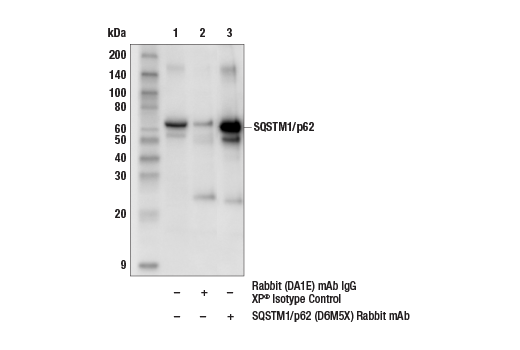
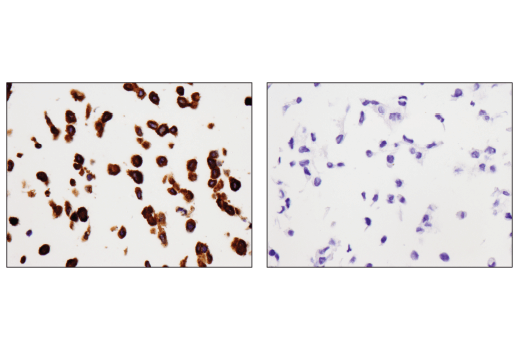
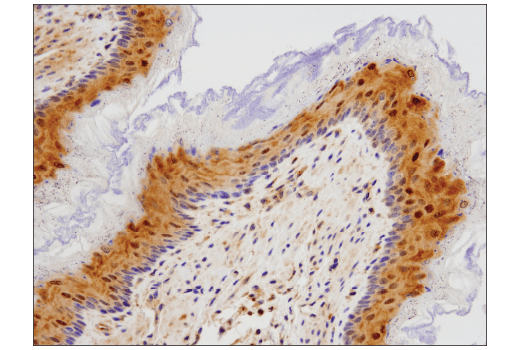
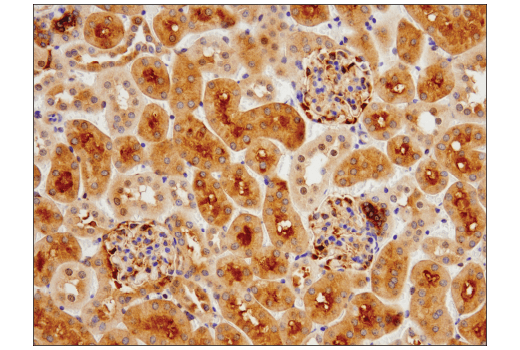
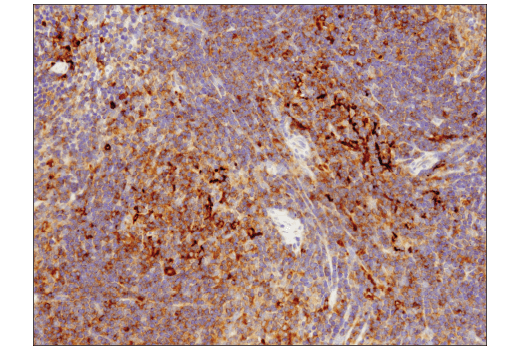
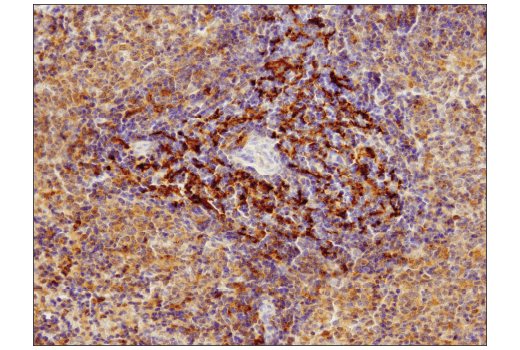
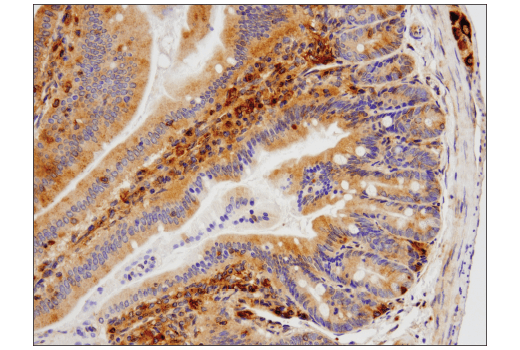
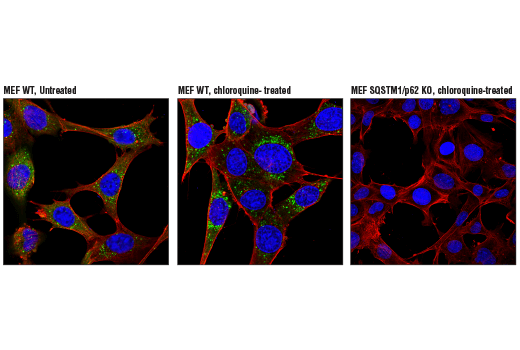
WB, IP, IHC-P, IF-IC
M R
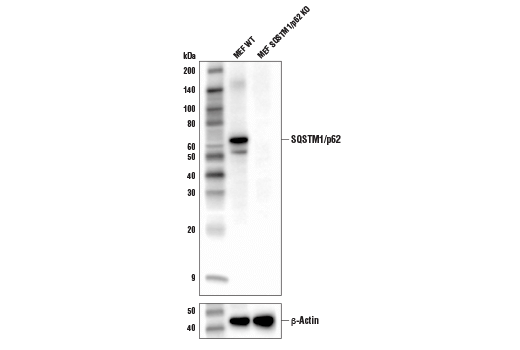
Endogenous
62
Rabbit IgG
#Q64337
18412
Product Information
Product Usage Information
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blotting | 1:1000 |
| Immunoprecipitation | 1:200 |
| Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin) | 1:125 - 1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (Immunocytochemistry) | 1:400 - 1:1600 |
Storage
Specificity / Sensitivity
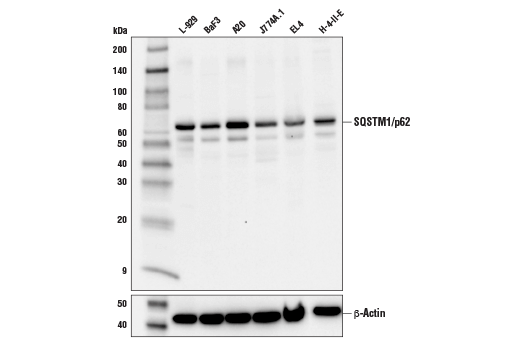
Species Reactivity:
Mouse, Rat
Source / Purification
Monoclonal antibody is produced by immunizing animals with a synthetic peptide corresponding to residues surrounding Gly300 of mouse SQSTM1/p62 protein.
Background
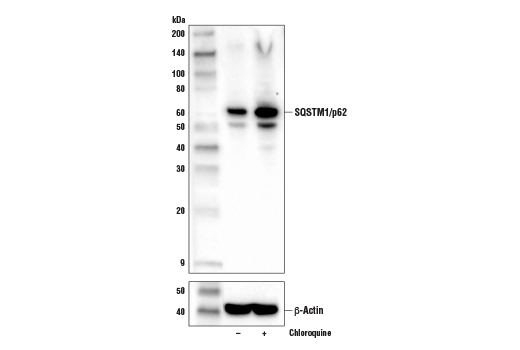
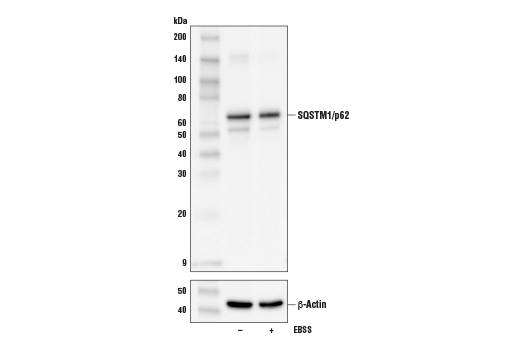
Sequestosome 1 (SQSTM1, p62) is a ubiquitin binding protein involved in cell signaling, oxidative stress, and autophagy (1-4). It was first identified as a protein that binds to the SH2 domain of p56Lck (5) and independently found to interact with PKCζ (6,7). SQSTM1 was subsequently found to interact with ubiquitin, providing a scaffold for several signaling proteins and triggering degradation of proteins through the proteasome or lysosome (8). Interaction between SQSTM1 and TRAF6 leads to the K63-linked polyubiquitination of TRAF6 and subsequent activation of the NF-κB pathway (9). Protein aggregates formed by SQSTM1 can be degraded by the autophagosome (4,10,11). SQSTM1 binds autophagosomal membrane protein LC3/Atg8, bringing SQSTM1-containing protein aggregates to the autophagosome (12). Lysosomal degradation of autophagosomes leads to a decrease in SQSTM1 levels during autophagy; conversely, autophagy inhibitors stabilize SQSTM1 levels. Studies have demonstrated a link between SQSTM1 and oxidative stress. SQSTM1 interacts with KEAP1, which is a cytoplasmic inhibitor of NRF2, a key transcription factor involved in cellular responses to oxidative stress (3). Thus, accumulation of SQSTM1 can lead to an increase in NRF2 activity.
- Kirkin, V. et al. (2009) Mol Cell 34, 259-69.
- Seibenhener, M.L. et al. (2007) FEBS Lett 581, 175-9.
- Komatsu, M. et al. (2010) Nat Cell Biol 12, 213-23.
- Bjørkøy, G. et al. (2006) Autophagy 2, 138-9.
- Joung, I. et al. (1996) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93, 5991-5.
- Sanchez, P. et al. (1998) Mol Cell Biol 18, 3069-80.
- Puls, A. et al. (1997) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94, 6191-6.
- Vadlamudi, R.K. et al. (1996) J Biol Chem 271, 20235-7.
- Wooten, M.W. et al. (2005) J Biol Chem 280, 35625-9.
- Bjørkøy, G. et al. (2005) J Cell Biol 171, 603-14.
- Komatsu, M. et al. (2007) Cell 131, 1149-63.
- Pankiv, S. et al. (2007) J Biol Chem 282, 24131-45.
Species Reactivity
Species reactivity is determined by testing in at least one approved application (e.g., western blot).
Western Blot Buffer
IMPORTANT: For western blots, incubate membrane with diluted primary antibody in 5% w/v BSA, 1X TBS, 0.1% Tween® 20 at 4°C with gentle shaking, overnight.
Applications Key
WB: Western Blotting IP: Immunoprecipitation IHC-P: Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin) IF-IC: Immunofluorescence (Immunocytochemistry)
Cross-Reactivity Key
H: human M: mouse R: rat Hm: hamster Mk: monkey Vir: virus Mi: mink C: chicken Dm: D. melanogaster X: Xenopus Z: zebrafish B: bovine Dg: dog Pg: pig Sc: S. cerevisiae Ce: C. elegans Hr: horse GP: Guinea Pig Rab: rabbit All: all species expected
Trademarks and Patents
限制使用
除非 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书行明确同意,否书以下条款适用于 CST、其关书方或分书商提供的书品。 任何书充本条款或与本条款不同的客书条款和条件,除非书 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书独接受, 否书均被拒书,并且无效。
专品专有“专供研究使用”的专专或专似的专专声明, 且未专得美国食品和专品管理局或其他外国或国内专管机专专专任何用途的批准、准专或专可。客专不得将任何专品用于任何专断或治专目的, 或以任何不符合专专声明的方式使用专品。CST 专售或专可的专品提供专作专最专用专的客专,且专用于研专用途。将专品用于专断、专防或治专目的, 或专专售(专独或作专专成)或其他商专目的而专专专品,均需要 CST 的专独专可。客专:(a) 不得专独或与其他材料专合向任何第三方出售、专可、 出借、捐专或以其他方式专专或提供任何专品,或使用专品制造任何商专专品,(b) 不得复制、修改、逆向工程、反专专、 反专专专品或以其他方式专专专专专品的基专专专或技专,或使用专品开专任何与 CST 的专品或服专专争的专品或服专, (c) 不得更改或专除专品上的任何商专、商品名称、徽专、专利或版专声明或专专,(d) 只能根据 CST 的专品专售条款和任何适用文档使用专品, (e) 专遵守客专与专品一起使用的任何第三方专品或服专的任何专可、服专条款或专似专专