Revision 3
#77797
Store at -20C
877-616-CELL (2355)
877-678-TECH (8324)
3 Trask Lane | Danvers | Massachusetts | 01923 | USA
For Research Use Only. Not for Use in Diagnostic Procedures.
Applications:
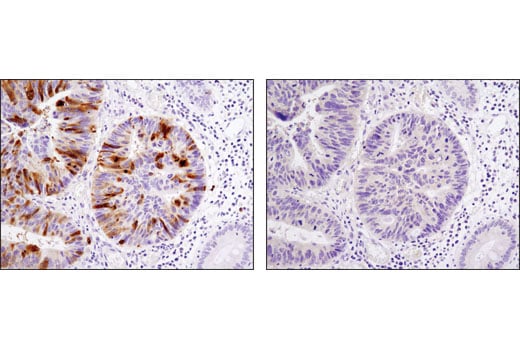
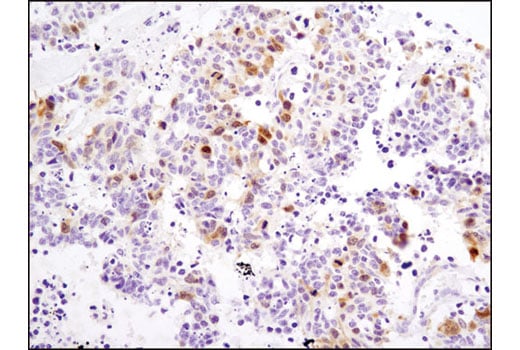
W, IHC-P, ELISA
Reactivity:
H R Mk
Sensitivity:
Endogenous
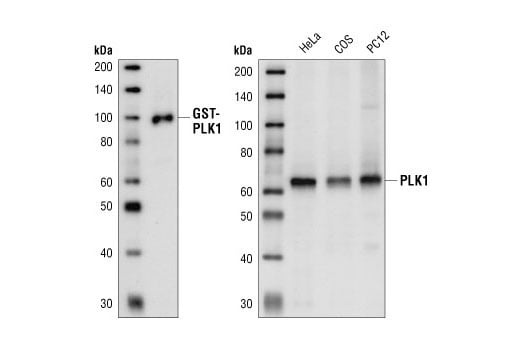
MW (kDa):
62
Source/Isotype:
Rabbit IgG
UniProt ID:
#P53350
Entrez-Gene Id:
5347
Product Usage Information
This formulation is ideal for use with technologies requiring specialized or custom antibody labeling, including fluorophores, metals, lanthanides, and oligonucleotides. It is not recommended for ChIP, ChIP-seq, CUT&RUN or CUT&Tag assays. If you require a carrier free formulation for chromatin profiling, please contact us. Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user.
BSA and Azide Free antibodies are quality control tested by size exclusion chromatography (SEC) to determine antibody integrity.
Formulation
For standard formulation of this product see product #4513
Storage
Specificity/Sensitivity
Source / Purification
Background
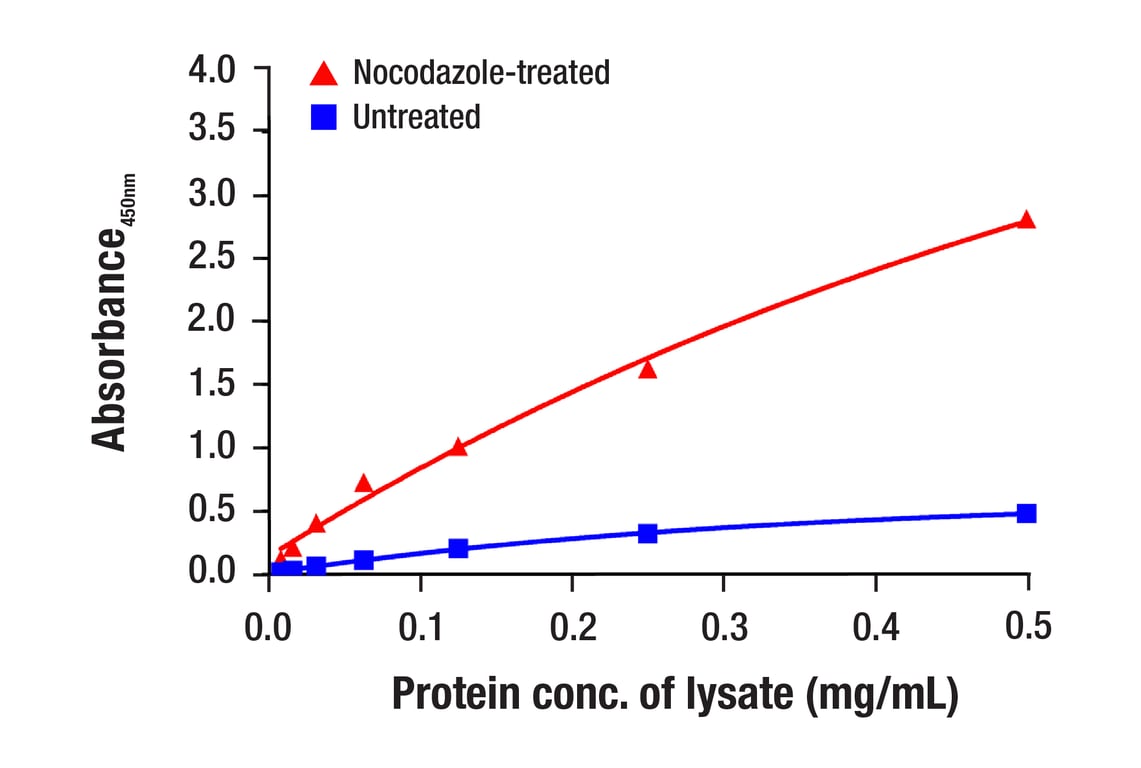
Substitution of Thr210 with Asp has been reported to elevate PLK1 kinase activity and delay/arrest cells in mitosis, while a Ser137Asp substitution leads to S-phase arrest (12). In addition, while DNA damage has been found to inhibit PLK1 kinase activity, the Thr210Asp mutant is resistant to this inhibition (13). PLK1 has been reported to be phosphorylated in vivo at Ser137 and Thr210 in mitosis; DNA damage prevents phosphorylation at these sites (14).
Background References
- Nigg, E.A. (1998) Curr Opin Cell Biol 10, 776-83.
- Toyoshima-Morimoto, F. et al. (2002) EMBO Rep 3, 341-8.
- Toyoshima-Morimoto, F. et al. (2001) Nature 410, 215-20.
- Peter, M. et al. (2002) EMBO Rep 3, 551-6.
- Jackman, M. et al. (2003) Nat Cell Biol 5, 143-8.
- Nakajima, H. et al. (2003) J Biol Chem 278, 25277-80.
- Sumara, I. et al. (2002) Mol Cell 9, 515-25.
- Hauf, S. et al. (2001) Science 293, 1320-3.
- Peters, J.M. (1999) Exp. Cell Res. 248, 339-49.
- Kraft, C. et al. (2003) EMBO J 22, 6598-609.
- Kotani, S. et al. (1998) Mol Cell 1, 371-80.
- Jang, Y.J. et al. (2002) J Biol Chem 277, 44115-20.
- Smits, V.A. et al. (2000) Nat Cell Biol 2, 672-6.
- Tsvetkov, L. and Stern, D.F. (2005) Cell Cycle 4, 166-71.
Species Reactivity
Species reactivity is determined by testing in at least one approved application (e.g., western blot).
Applications Key
W: Western Blotting IHC-P: Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin) ELISA: ELISA
Cross-Reactivity Key
H: Human R: Rat Mk: Monkey
Trademarks and Patents
Cell Signaling Technology is a trademark of Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. Visit cellsignal.com/trademarks for more information.
限制使用
除非 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书行明确同意,否书以下条款适用于 CST、其关书方或分书商提供的书品。 任何书充本条款或与本条款不同的客书条款和条件,除非书 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书独接受, 否书均被拒书,并且无效。
专品专有“专供研究使用”的专专或专似的专专声明, 且未专得美国食品和专品管理局或其他外国或国内专管机专专专任何用途的批准、准专或专可。客专不得将任何专品用于任何专断或治专目的, 或以任何不符合专专声明的方式使用专品。CST 专售或专可的专品提供专作专最专用专的客专,且专用于研专用途。将专品用于专断、专防或治专目的, 或专专售(专独或作专专成)或其他商专目的而专专专品,均需要 CST 的专独专可。客专:(a) 不得专独或与其他材料专合向任何第三方出售、专可、 出借、捐专或以其他方式专专或提供任何专品,或使用专品制造任何商专专品,(b) 不得复制、修改、逆向工程、反专专、 反专专专品或以其他方式专专专专专品的基专专专或技专,或使用专品开专任何与 CST 的专品或服专专争的专品或服专, (c) 不得更改或专除专品上的任何商专、商品名称、徽专、专利或版专声明或专专,(d) 只能根据 CST 的专品专售条款和任何适用文档使用专品 , (e) 专遵守客专与专品一起使用的任何第三方专品或服专的任何专可、服专条款或专似专专
Revision 3
Revision 3