WB, IF-F
H M R
Endogenous
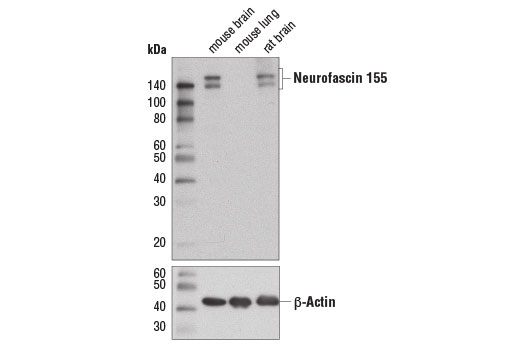
140-155
Rabbit IgG
#O94856
23114
Product Information
Product Usage Information
This formulation is ideal for use with technologies requiring specialized or custom antibody labeling, including fluorophores, metals, lanthanides, and oligonucleotides. It is not recommended for ChIP, ChIP-seq, CUT&RUN or CUT&Tag assays. If you require a carrier free formulation for chromatin profiling, please contact us. Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user.
Formulation
Storage
Specificity / Sensitivity
Species Reactivity:
Human, Mouse, Rat
Source / Purification
Monoclonal antibody is produced by immunizing animals with a synthetic peptide corresponding to residues surrounding Arg881 of human neurofascin 155 protein.
Background
Myelinated axons contain un-myelinated gaps called nodes of Ranvier. These regularly spaced gaps are critical for the proper propagation and rapid conduction of nerve impulses in the central and peripheral nervous system (1). The structure and organization of the nodes of Ranvier is dictated by interaction between the axon and glial cells (2). Voltage-gated sodium channels concentrated at the nodes and potassium channels clustered at the paranodes are responsible for propagation of the action potentials (3,4). Other proteins that contribute to the architecture and function of the nodes of Ranvier include βIV spectrin (5), ankyrin-G (6), and the L1 cell adhesion molecules, neurofascin and NrCAM (7,8).
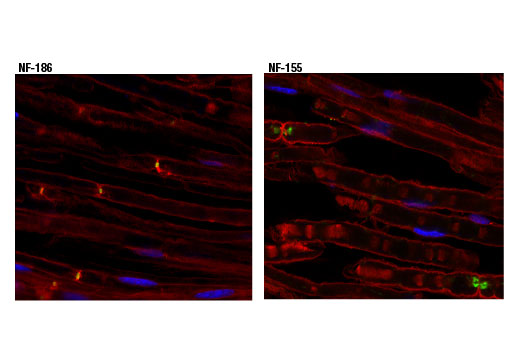
Alternative splicing produces several neurofascin isoforms that differ in temporal and spatial expression. Neurofascin 186 is expressed in axons where it is concentrated at the nodes. Research studies indicate that neurofascin 186 is responsible for nodal assembly and clustering of sodium channels (9). Neurofascin 155 is expressed in glial cells and is localized to myelin paranodes. Interactions between neurofascin 155 and the contactin-associated protein (Caspr) tether the myelin sheath to the axon (10). N-linked glycosylation results in two forms of neurofascin 155 (high and low) that are differentially expressed during development (11).
- Black, J.A. et al. (1990) Trends Neurosci 13, 48-54.
- Salzer, J.L. (1997) Neuron 18, 843-6.
- Waxman, S.G. et al. (1989) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 86, 1406-10.
- Ritchie, J.M. (1992) Trends Neurosci 15, 345-51.
- Berghs, S. et al. (2000) J Cell Biol 151, 985-1002.
- Zhou, D. et al. (1998) J Cell Biol 143, 1295-304.
- Davis, J.Q. et al. (1996) J Cell Biol 135, 1355-67.
- Ratcliffe, C.F. et al. (2001) J Cell Biol 154, 427-34.
- Thaxton, C. et al. (2011) Neuron 69, 244-57.
- Charles, P. et al. (2002) Curr Biol 12, 217-20.
- Pomicter, A.D. et al. (2010) Brain 133, 389-405.
Species Reactivity
Species reactivity is determined by testing in at least one approved application (e.g., western blot).
Applications Key
WB: Western Blotting IF-F: Immunofluorescence (Frozen)
Cross-Reactivity Key
H: human M: mouse R: rat Hm: hamster Mk: monkey Vir: virus Mi: mink C: chicken Dm: D. melanogaster X: Xenopus Z: zebrafish B: bovine Dg: dog Pg: pig Sc: S. cerevisiae Ce: C. elegans Hr: horse GP: Guinea Pig Rab: rabbit All: all species expected
Trademarks and Patents
限制使用
除非 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书行明确同意,否书以下条款适用于 CST、其关书方或分书商提供的书品。 任何书充本条款或与本条款不同的客书条款和条件,除非书 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书独接受, 否书均被拒书,并且无效。
专品专有“专供研究使用”的专专或专似的专专声明, 且未专得美国食品和专品管理局或其他外国或国内专管机专专专任何用途的批准、准专或专可。客专不得将任何专品用于任何专断或治专目的, 或以任何不符合专专声明的方式使用专品。CST 专售或专可的专品提供专作专最专用专的客专,且专用于研专用途。将专品用于专断、专防或治专目的, 或专专售(专独或作专专成)或其他商专目的而专专专品,均需要 CST 的专独专可。客专:(a) 不得专独或与其他材料专合向任何第三方出售、专可、 出借、捐专或以其他方式专专或提供任何专品,或使用专品制造任何商专专品,(b) 不得复制、修改、逆向工程、反专专、 反专专专品或以其他方式专专专专专品的基专专专或技专,或使用专品开专任何与 CST 的专品或服专专争的专品或服专, (c) 不得更改或专除专品上的任何商专、商品名称、徽专、专利或版专声明或专专,(d) 只能根据 CST 的专品专售条款和任何适用文档使用专品, (e) 专遵守客专与专品一起使用的任何第三方专品或服专的任何专可、服专条款或专似专专