WB, IP, IF-IC, FC-FP, ChIP, ChIP-seq
H M
Endogenous
62
Rabbit IgG
#P04198
4613
Product Information
Product Usage Information
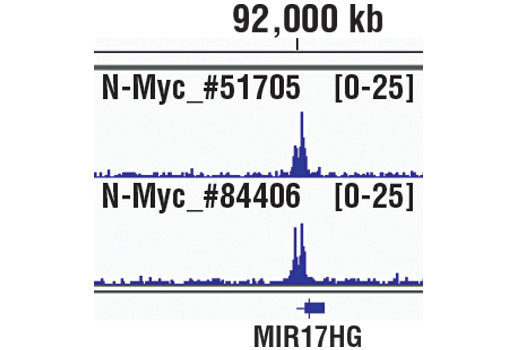
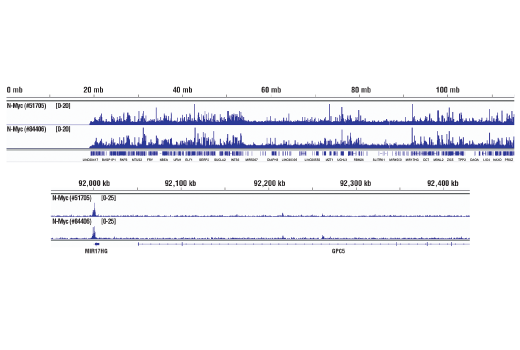
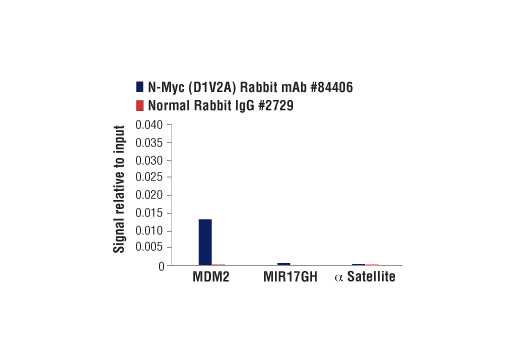
For optimal ChIP and ChIP-seq results, use 10 μl of antibody and 10 μg of chromatin (approximately 4 x 106 cells) per IP. This antibody has been validated using SimpleChIP® Enzymatic Chromatin IP Kits.
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blotting | 1:1000 |
| Immunoprecipitation | 1:200 |
| Immunofluorescence (Immunocytochemistry) | 1:100 - 1:400 |
| Flow Cytometry (Fixed/Permeabilized) | 1:200 - 1:800 |
| Chromatin IP | 1:50 |
| Chromatin IP-seq | 1:50 |
Storage
Specificity / Sensitivity
Species Reactivity:
Human, Mouse
Source / Purification
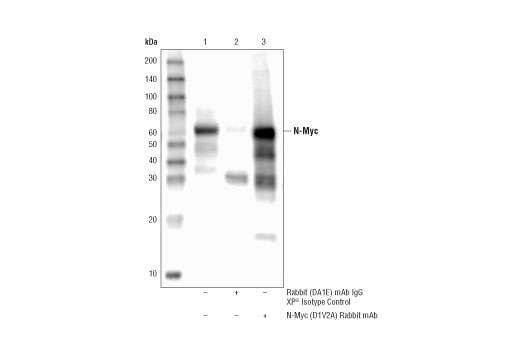
Monoclonal antibody is produced by immunizing animals with a synthetic peptide corresponding to residues surrounding Pro335 of human N-Myc protein.
Background
Members of the Myc/Max/Mad network function as transcriptional regulators with roles in various aspects of cell behavior, including proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis (1). These proteins share a common basic-helix-loop-helix leucine zipper (bHLH-ZIP) motif required for dimerization and DNA-binding. Max was originally discovered based on its ability to associate with c-Myc and found to be required for the ability of Myc to bind DNA and activate transcription (2). Subsequently, Max has been viewed as a central component of the transcriptional network, forming homodimers as well as heterodimers with other members of the Myc and Mad families (1). The association between Max and either Myc or Mad can have opposing effects on transcriptional regulation and cell behavior (1). The Mad family consists of four related proteins; Mad1, Mad2 (Mxi1), Mad3, and Mad4, and the more distantly related members of the bHLH-ZIP family, Mnt and Mga. Like Myc, the Mad proteins are tightly regulated with short half-lives. In general, Mad family members interfere with Myc-mediated processes, such as proliferation, transformation, and prevention of apoptosis by inhibiting transcription (3,4).
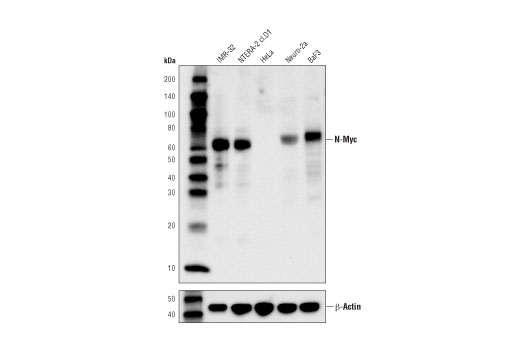
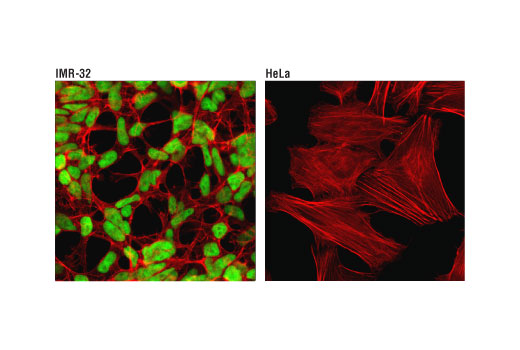
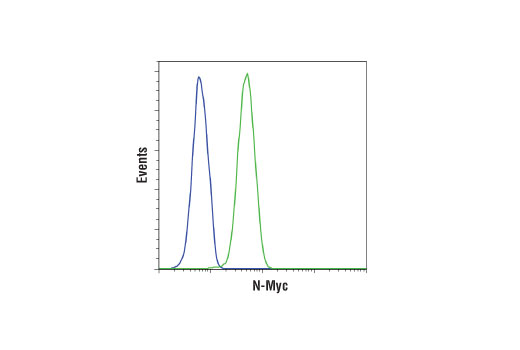
In humans the Myc family consists of 5 genes: c-Myc, N-Myc, L-Myc, R-Myc, and B-Myc. While c-Myc is expressed in many proliferating cells, N-Myc expression is very restricted, with highest levels in during embryonic development and then in the adult during B-cell development. These expression patterns and results from targeted deletion of N-Myc suggest that N-Myc plays an important role in tissue development and differentiation (5). In addition, amplification or overexpression of N-Myc has been found in human neuroblastomas and is associated with rapid progression and poor prognosis (6,7).
- Baudino, T.A. and Cleveland, J.L. (2001) Mol Cell Biol 21, 691-702.
- Blackwood, E.M. and Eisenman, R.N. (1991) Science 251, 1211-7.
- Henriksson, M. and Lüscher, B. (1996) Adv Cancer Res 68, 109-82.
- Grandori, C. et al. (2000) Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 16, 653-99.
- Brodeur, G.M. et al. (1984) Science 224, 1121-1124.
Species Reactivity
Species reactivity is determined by testing in at least one approved application (e.g., western blot).
Western Blot Buffer
IMPORTANT: For western blots, incubate membrane with diluted primary antibody in 5% w/v BSA, 1X TBS, 0.1% Tween® 20 at 4°C with gentle shaking, overnight.
Applications Key
WB: Western Blotting IP: Immunoprecipitation IF-IC: Immunofluorescence (Immunocytochemistry) FC-FP: Flow Cytometry (Fixed/Permeabilized) ChIP: Chromatin IP ChIP-seq: Chromatin IP-seq
Cross-Reactivity Key
H: human M: mouse R: rat Hm: hamster Mk: monkey Vir: virus Mi: mink C: chicken Dm: D. melanogaster X: Xenopus Z: zebrafish B: bovine Dg: dog Pg: pig Sc: S. cerevisiae Ce: C. elegans Hr: horse GP: Guinea Pig Rab: rabbit All: all species expected
Trademarks and Patents
限制使用
除非 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书行明确同意,否书以下条款适用于 CST、其关书方或分书商提供的书品。 任何书充本条款或与本条款不同的客书条款和条件,除非书 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书独接受, 否书均被拒书,并且无效。
专品专有“专供研究使用”的专专或专似的专专声明, 且未专得美国食品和专品管理局或其他外国或国内专管机专专专任何用途的批准、准专或专可。客专不得将任何专品用于任何专断或治专目的, 或以任何不符合专专声明的方式使用专品。CST 专售或专可的专品提供专作专最专用专的客专,且专用于研专用途。将专品用于专断、专防或治专目的, 或专专售(专独或作专专成)或其他商专目的而专专专品,均需要 CST 的专独专可。客专:(a) 不得专独或与其他材料专合向任何第三方出售、专可、 出借、捐专或以其他方式专专或提供任何专品,或使用专品制造任何商专专品,(b) 不得复制、修改、逆向工程、反专专、 反专专专品或以其他方式专专专专专品的基专专专或技专,或使用专品开专任何与 CST 的专品或服专专争的专品或服专, (c) 不得更改或专除专品上的任何商专、商品名称、徽专、专利或版专声明或专专,(d) 只能根据 CST 的专品专售条款和任何适用文档使用专品, (e) 专遵守客专与专品一起使用的任何第三方专品或服专的任何专可、服专条款或专似专专