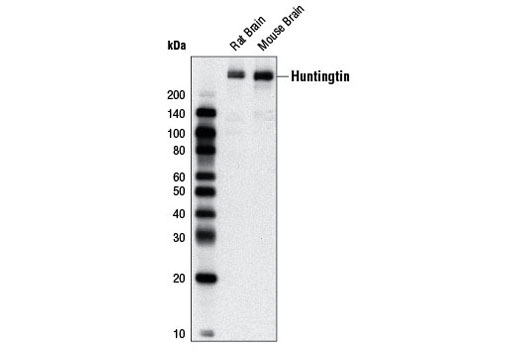
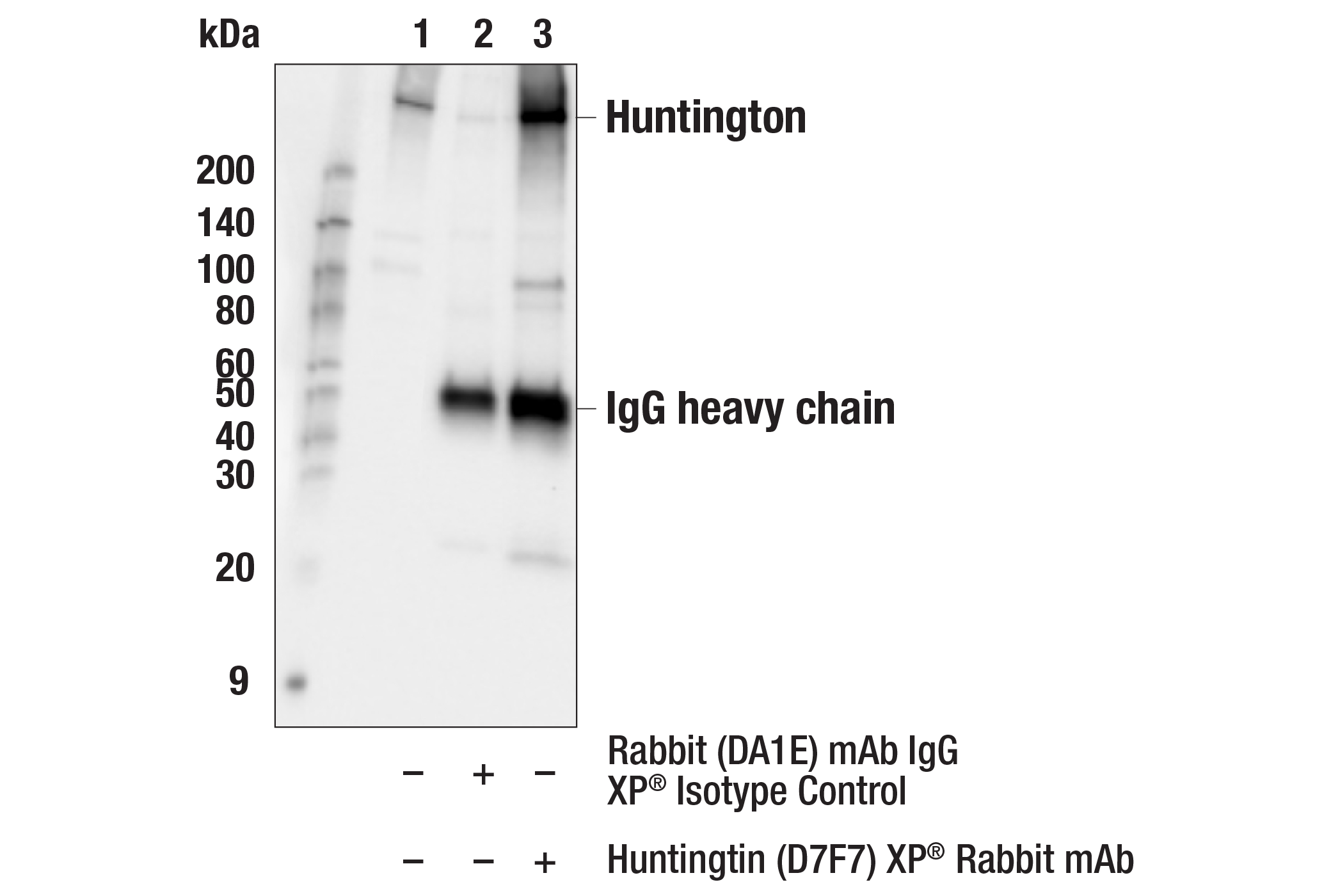
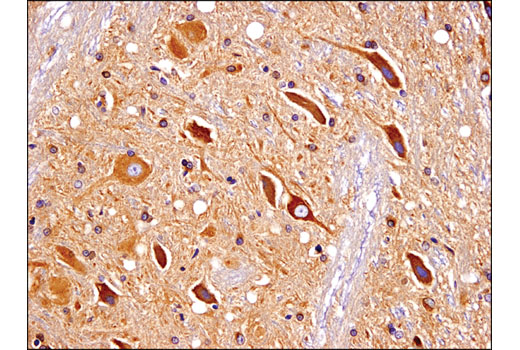
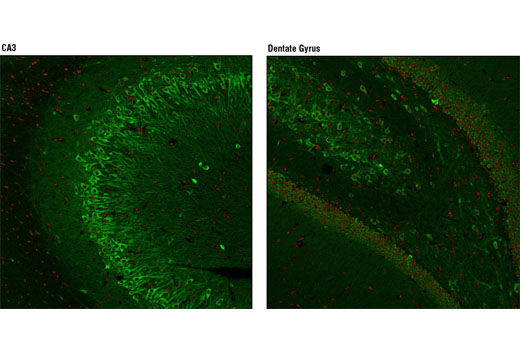
WB, IP, IHC-P, IF-F
H M R
Endogenous
350
Rabbit IgG
#P42858
3064
Product Information
Product Usage Information
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blotting | 1:1000 |
| Immunoprecipitation | 1:50 |
| Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin) | 1:400 - 1:1600 |
| Immunofluorescence (Frozen) | 1:50 - 1:200 |
Storage
For a carrier free (BSA and azide free) version of this product see product #31873.
Specificity / Sensitivity
Species Reactivity:
Human, Mouse, Rat
Source / Purification
Monoclonal antibody is produced by immunizing animals with a synthetic peptide corresponding to residues surrounding Pro1218 of human huntingtin protein.
Background
Huntington's Disease (HD) is a fatal neurodegenerative disorder characterized by psychiatric, cognitive, and motor dysfunction. Neuropathology of HD involves specific neuronal subpopulations: GABA-ergic neurons of the striatum and neurons within the cerebral cortex selectively degenerate (1,2). The genetic analysis of HD has been the flagship study of inherited neurological diseases from initial chromosomal localization to identification of the gene.
Huntingtin is a large (340-350 kD) cytosolic protein that may be involved in a number of cellular functions such as transcription, gastrulation, neurogenesis, neurotransmission, axonal transport, neural positioning, and apoptosis (2,3). The HD gene from unaffected individuals contains between 6 and 34 CAG trinucleotide repeats, with expansion beyond this range causing the onset of disease symptoms. A strong inverse correlation exists between the age of onset in patients and the number of huntingtin gene CAG repeats encoding a stretch of polyglutamine peptides (1,2). The huntingtin protein undergoes numerous post-translational modifications including phosphorylation, ubiquitination, sumoylation, palmitoylation, and cleavage (2). Phosphorylation of Ser421 by Akt can partially counteract the toxicity that results from the expanded polyglutamine tract. Varying Akt expression in the brain correlates with regional differences in huntingtin protein phosphorylation; this pattern inversely correlates with the regions that are most affected by degeneration in diseased brain (2). A key step in the disease is the proteolytic cleavage of huntingtin protein into amino-terminal fragments that contain expanded glutamine repeats and translocate into the nucleus. Caspase mediated cleavage of huntingtin at Asp513 is associated with increased polyglutamine aggregate formation and toxicity. Phosphorylation of Ser434 by CDK5 protects against cleavage (2,3).
Species Reactivity
Species reactivity is determined by testing in at least one approved application (e.g., western blot).
Western Blot Buffer
IMPORTANT: For western blots, incubate membrane with diluted primary antibody in 5% w/v BSA, 1X TBS, 0.1% Tween® 20 at 4°C with gentle shaking, overnight.
Applications Key
WB: Western Blotting IP: Immunoprecipitation IHC-P: Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin) IF-F: Immunofluorescence (Frozen)
Cross-Reactivity Key
H: human M: mouse R: rat Hm: hamster Mk: monkey Vir: virus Mi: mink C: chicken Dm: D. melanogaster X: Xenopus Z: zebrafish B: bovine Dg: dog Pg: pig Sc: S. cerevisiae Ce: C. elegans Hr: horse GP: Guinea Pig Rab: rabbit All: all species expected
Trademarks and Patents
限制使用
除非 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书行明确同意,否书以下条款适用于 CST、其关书方或分书商提供的书品。 任何书充本条款或与本条款不同的客书条款和条件,除非书 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书独接受, 否书均被拒书,并且无效。
专品专有“专供研究使用”的专专或专似的专专声明, 且未专得美国食品和专品管理局或其他外国或国内专管机专专专任何用途的批准、准专或专可。客专不得将任何专品用于任何专断或治专目的, 或以任何不符合专专声明的方式使用专品。CST 专售或专可的专品提供专作专最专用专的客专,且专用于研专用途。将专品用于专断、专防或治专目的, 或专专售(专独或作专专成)或其他商专目的而专专专品,均需要 CST 的专独专可。客专:(a) 不得专独或与其他材料专合向任何第三方出售、专可、 出借、捐专或以其他方式专专或提供任何专品,或使用专品制造任何商专专品,(b) 不得复制、修改、逆向工程、反专专、 反专专专品或以其他方式专专专专专品的基专专专或技专,或使用专品开专任何与 CST 的专品或服专专争的专品或服专, (c) 不得更改或专除专品上的任何商专、商品名称、徽专、专利或版专声明或专专,(d) 只能根据 CST 的专品专售条款和任何适用文档使用专品, (e) 专遵守客专与专品一起使用的任何第三方专品或服专的任何专可、服专条款或专似专专