| Product Includes | Product # | Quantity | Mol. Wt | Isotype/Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
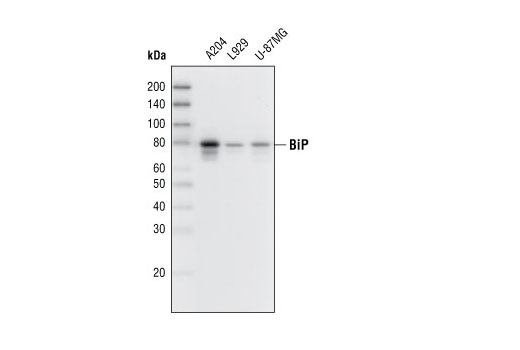
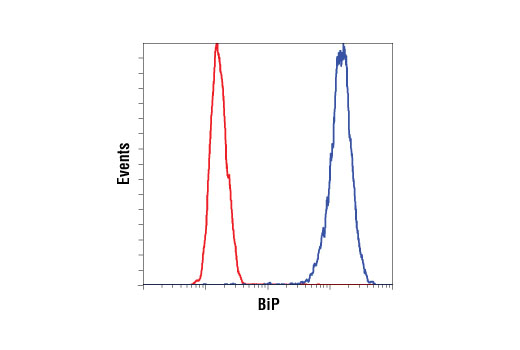
| BiP (C50B12) Rabbit mAb | 3177 | 20 µl | 78 kDa | Rabbit IgG |
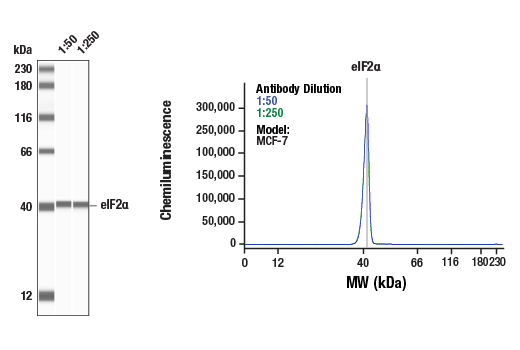
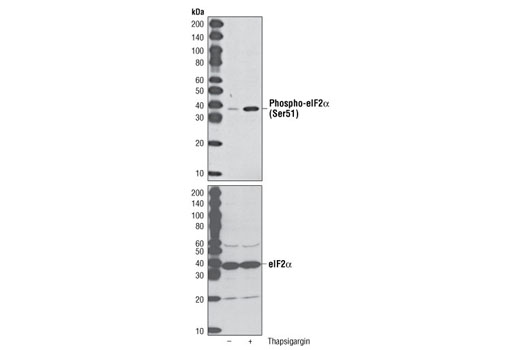
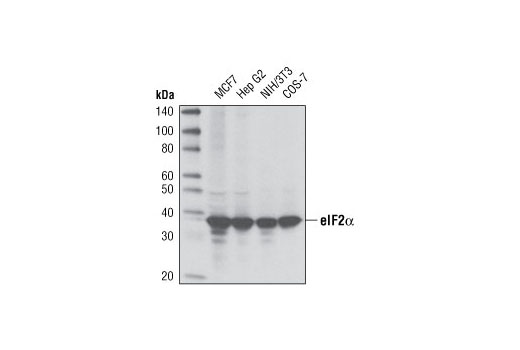
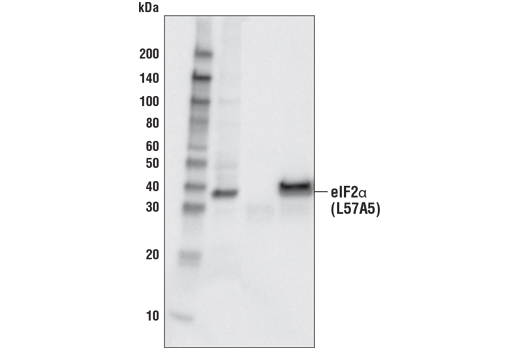
| eIF2α (D7D3) XP® Rabbit mAb | 5324 | 20 µl | 38 kDa | Rabbit IgG |
| Phospho-eIF2α (Ser51) (D9G8) XP® Rabbit mAb | 3398 | 20 µl | 38 kDa | Rabbit IgG |
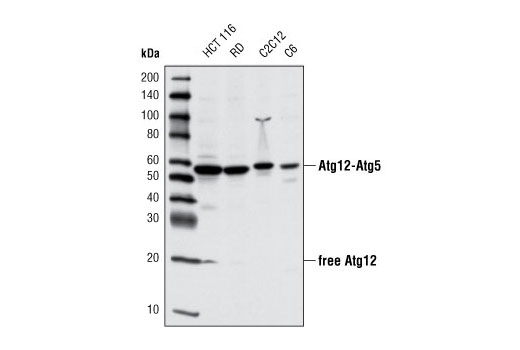
| Atg12 (D88H11) Rabbit mAb | 4180 | 20 µl | 16, 55 kDa | Rabbit IgG |
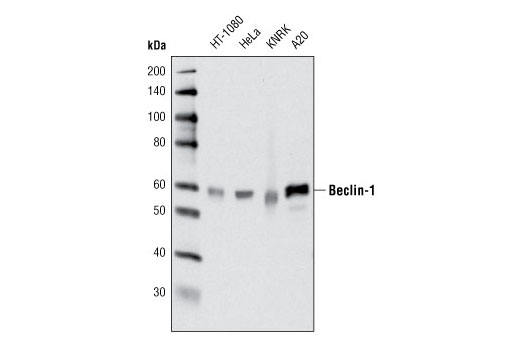
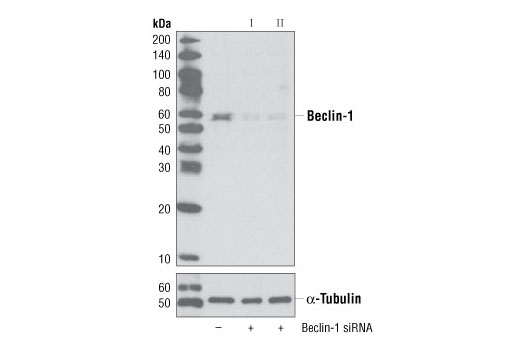
| Beclin-1 (D40C5) Rabbit mAb | 3495 | 20 µl | 60 kDa | Rabbit IgG |
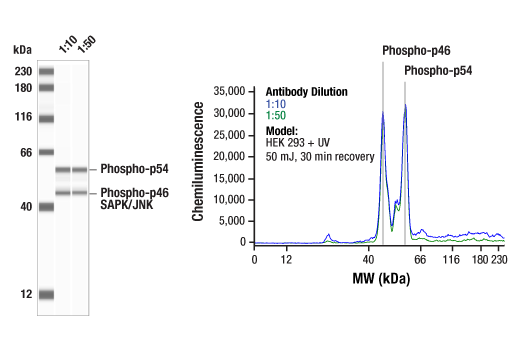
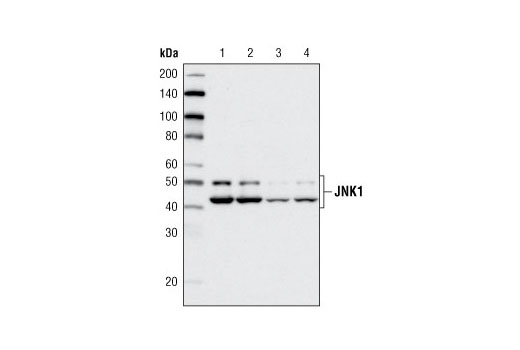
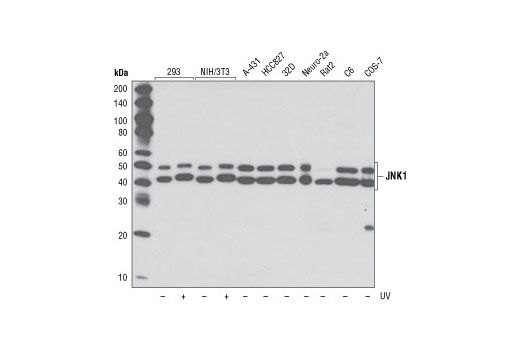
| JNK1 (2C6) Mouse mAb | 3708 | 20 µl | 46, 54 kDa | Mouse IgG1 |
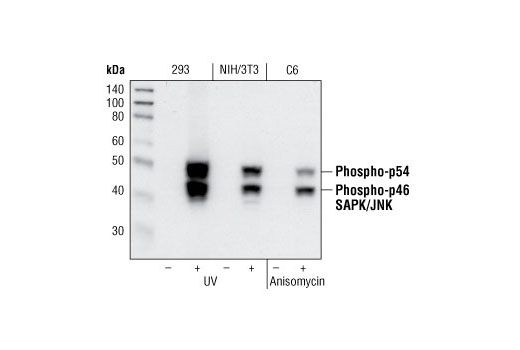
| Phospho-SAPK/JNK (Thr183/Tyr185) (81E11) Rabbit mAb | 4668 | 20 µl | 46, 54 kDa | Rabbit IgG |
| Anti-rabbit IgG, HRP-linked Antibody | 7074 | 100 µl | Goat | |
| Anti-mouse IgG, HRP-linked Antibody | 7076 | 100 µl | Horse |
Please visit cellsignal.com for individual component applications, species cross-reactivity, dilutions, protocols, and additional product information.
Description
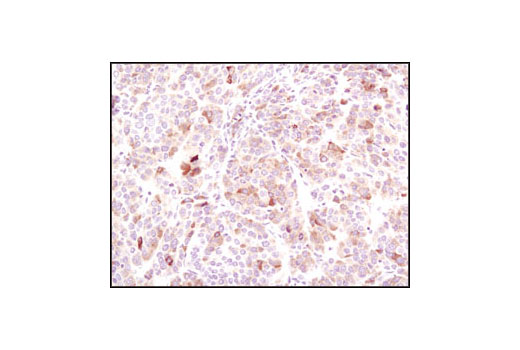
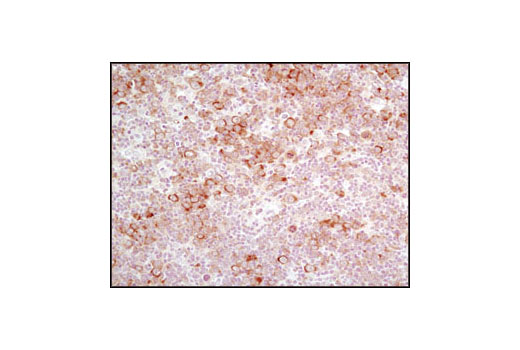
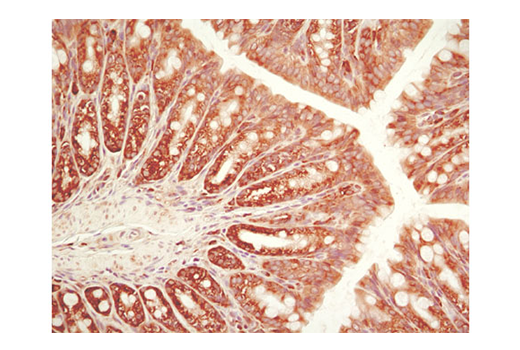
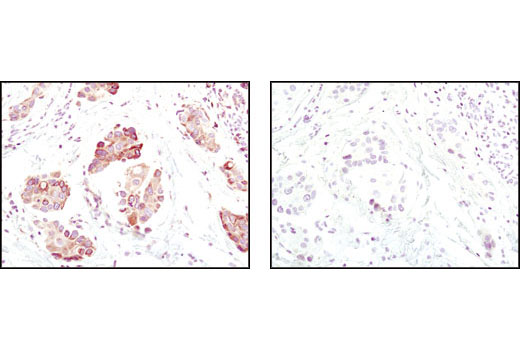
The ER Stress-induced Antibody Sampler Kit contains reagents to investigate ER stress-induced signaling within the cell. The kit contains enough primary antibodies to perform four western blot experiments per primary antibody.
Storage
Background
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is an organelle with essential biosynthetic and signaling functions in eukaryotic cells (1). Post synthesis of secretory and transmembrane proteins on polysomes, proteins are translocated into the ER where they are often modified by disulfide bond formation, amino-linked glycosylation, and folding. Different physiological and pathological conditions can disturb proper protein folding in the ER causing ER stress (1). ER stress activates an intracellular signaling transduction pathway called unfolded protein response (UPR) and autophagy to avoid cell death (2). The main role of UPR is to improve the protein load on the ER by shutting down protein translation and gene transcription to enhance ER's folding capacity (2). On the other hand, autophagy is a catabolic process for the autophagosomic-lysosomal degradation of bulk cytoplasmc contents (3,4). One of the chaperones aiding in proper protein folding is Binding immunoglobulin Protein (BiP) (5,6). BiP works by binding to misfolded proteins to prevent them from forming aggregates and assists in proper refolding (7). The molecular machinery of autophagy was largely discovered in yeast and referred to as autophagy-related (Atg) genes. Formation of the autophagosome involves a ubiquitin-like conjugation system in which Atg12 is covalently bound to Atg5 and targeted to autophagosome vesicles (8-10). One of the proteins critical to autophagy process is Beclin-1, the mammalian orthologue of the yeast autophagy protein Apg6/Vps30 (11). Beclin-1 can complement defects in yeast autophagy caused by loss of Apg6 and can also stimulate autophagy when overexpressed in mammalian cells (12). Mammalian Beclin-1 was originally isolated in a yeast two-hybrid screen for Bcl-2 interacting proteins and has been shown to interact with Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL, but not with Bax or Bak (13). Phosphorylation of the eukaryotic initiation factor 2 (eIF2) α subunit is a well-documented mechanism to downregulate protein synthesis under a variety of stress conditions. eIF2 binds GTP and Met-tRNAi and transfers Met-tRNA to the 40S subunit to form the 43S preinitiation complex (14,15). Kinases that are activated by viral infection (PKR) can phosphorylate the α subunit of eIF2 (16,17). Induction of PKR by IFN-γ and TNF-α induces potent phosphorylation of eIF2α at Ser51 (18,19). There are three SAPK/JNK genes each of which undergoes alternative splicing, resulting in numerous isoforms (20). The IRE1, a transmembrane serine/threonine kinase (21,22), through its kinase activity activates SAPK/JNK in the early stage of ER stress in order to induce autophagosome formation (23).
- Verfaillie, T. et al. (2010) Int J Cell Biol 2010, 930509.
- Ogata, M. et al. (2006) Mol Cell Biol 26, 9220-31.
- Reggiori, F. and Klionsky, D.J. (2002) Eukaryot Cell 1, 11-21.
- Codogno, P. and Meijer, A.J. (2005) Cell Death Differ 12 Suppl 2, 1509-18.
- Wabl, M. and Steinberg, C. (1982) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 79, 6976-8.
- Haas, I.G. and Wabl, M. (2002) Nature 306, 387-9.
- Kohno, K. et al. (1993) Mol Cell Biol 13, 877-90.
- Mizushima, N. et al. (1998) J Biol Chem 273, 33889-92.
- Mizushima, N. et al. (1998) Nature 395, 395-8.
- Suzuki, K. et al. (2001) EMBO J 20, 5971-81.
- Kametaka, S. et al. (1998) J Biol Chem 273, 22284-91.
- Liang, X.H. et al. (1999) Nature 402, 672-6.
- Liang, X.H. et al. (1998) J Virol 72, 8586-96.
- Kimball, S.R. (1999) Int J Biochem Cell Biol 31, 25-9.
- de Haro, C. et al. (1996) FASEB J 10, 1378-87.
- Kaufman, R.J. (1999) Genes Dev 13, 1211-33.
- Sheikh, M.S. and Fornace, A.J. (1999) Oncogene 18, 6121-8.
- Cheshire, J.L. et al. (1999) J Biol Chem 274, 4801-6.
- Zamanian-Daryoush, M. et al. (2000) Mol Cell Biol 20, 1278-90.
- Kyriakis, J.M. and Avruch, J. (2001) Physiol Rev 81, 807-69.
- Nikawa, J. and Yamashita, S. (1992) Mol Microbiol 6, 1441-6.
- Cox, J.S. et al. (1993) Cell 73, 1197-206.
- Urano, F. et al. (2000) Science 287, 664-6.
Background References
Trademarks and Patents
限制使用
除非 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书行明确同意,否书以下条款适用于 CST、其关书方或分书商提供的书品。 任何书充本条款或与本条款不同的客书条款和条件,除非书 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书独接受, 否书均被拒书,并且无效。
专品专有“专供研究使用”的专专或专似的专专声明, 且未专得美国食品和专品管理局或其他外国或国内专管机专专专任何用途的批准、准专或专可。客专不得将任何专品用于任何专断或治专目的, 或以任何不符合专专声明的方式使用专品。CST 专售或专可的专品提供专作专最专用专的客专,且专用于研专用途。将专品用于专断、专防或治专目的, 或专专售(专独或作专专成)或其他商专目的而专专专品,均需要 CST 的专独专可。客专:(a) 不得专独或与其他材料专合向任何第三方出售、专可、 出借、捐专或以其他方式专专或提供任何专品,或使用专品制造任何商专专品,(b) 不得复制、修改、逆向工程、反专专、 反专专专品或以其他方式专专专专专品的基专专专或技专,或使用专品开专任何与 CST 的专品或服专专争的专品或服专, (c) 不得更改或专除专品上的任何商专、商品名称、徽专、专利或版专声明或专专,(d) 只能根据 CST 的专品专售条款和任何适用文档使用专品, (e) 专遵守客专与专品一起使用的任何第三方专品或服专的任何专可、服专条款或专似专专