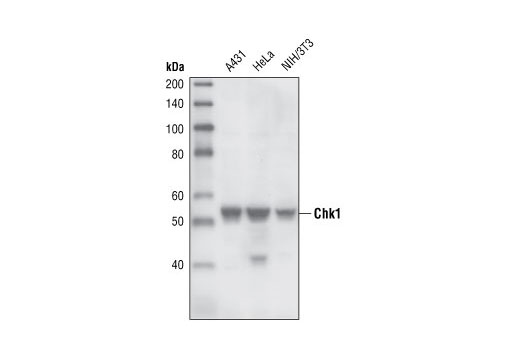
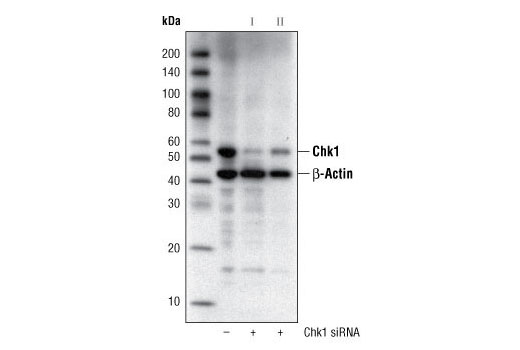
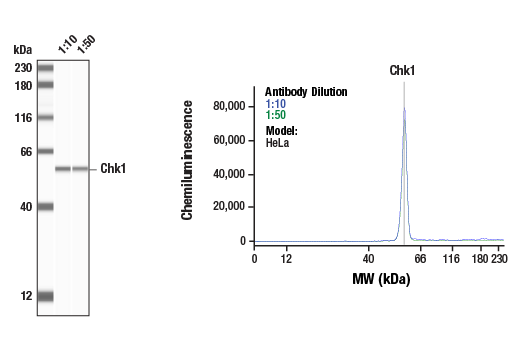
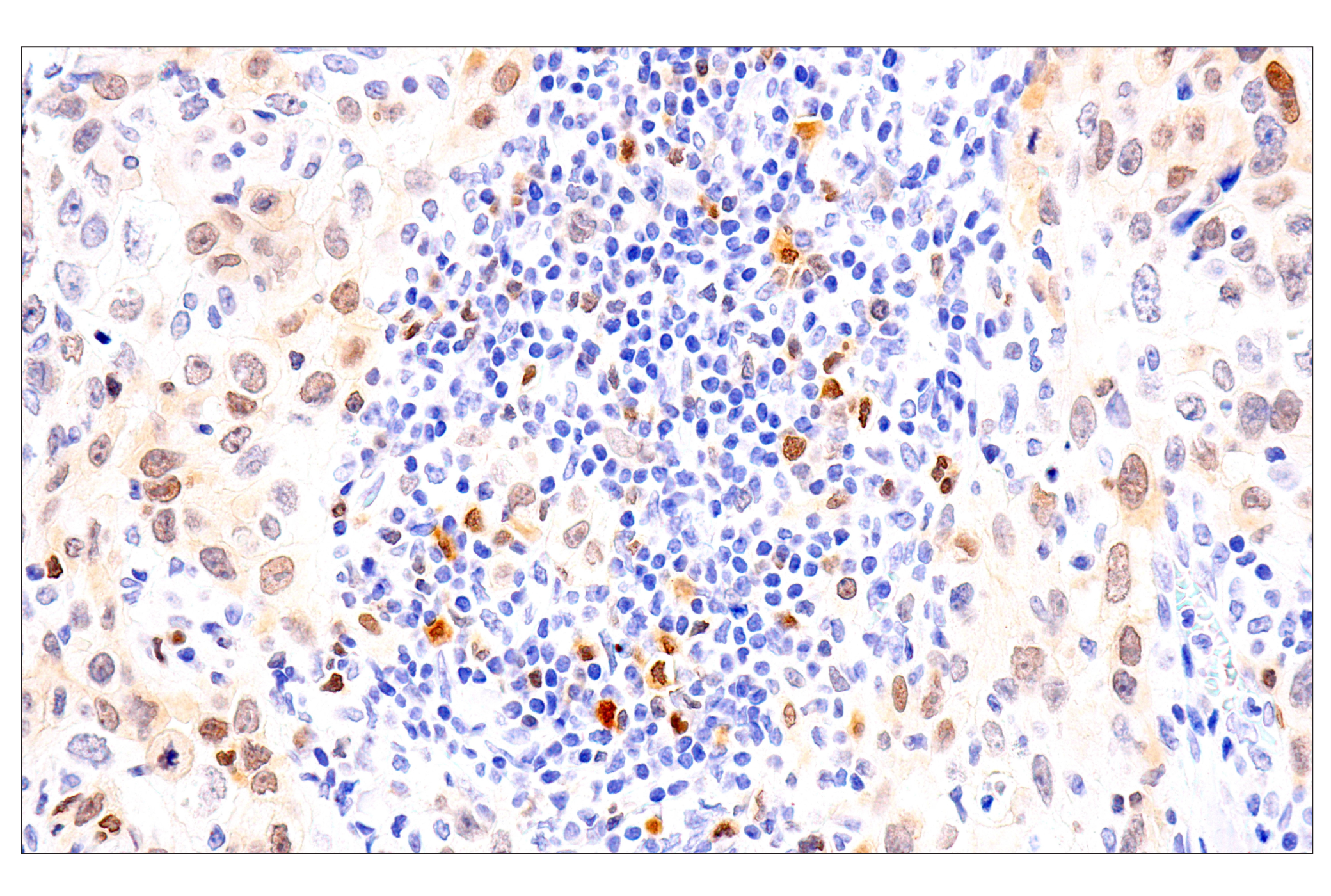
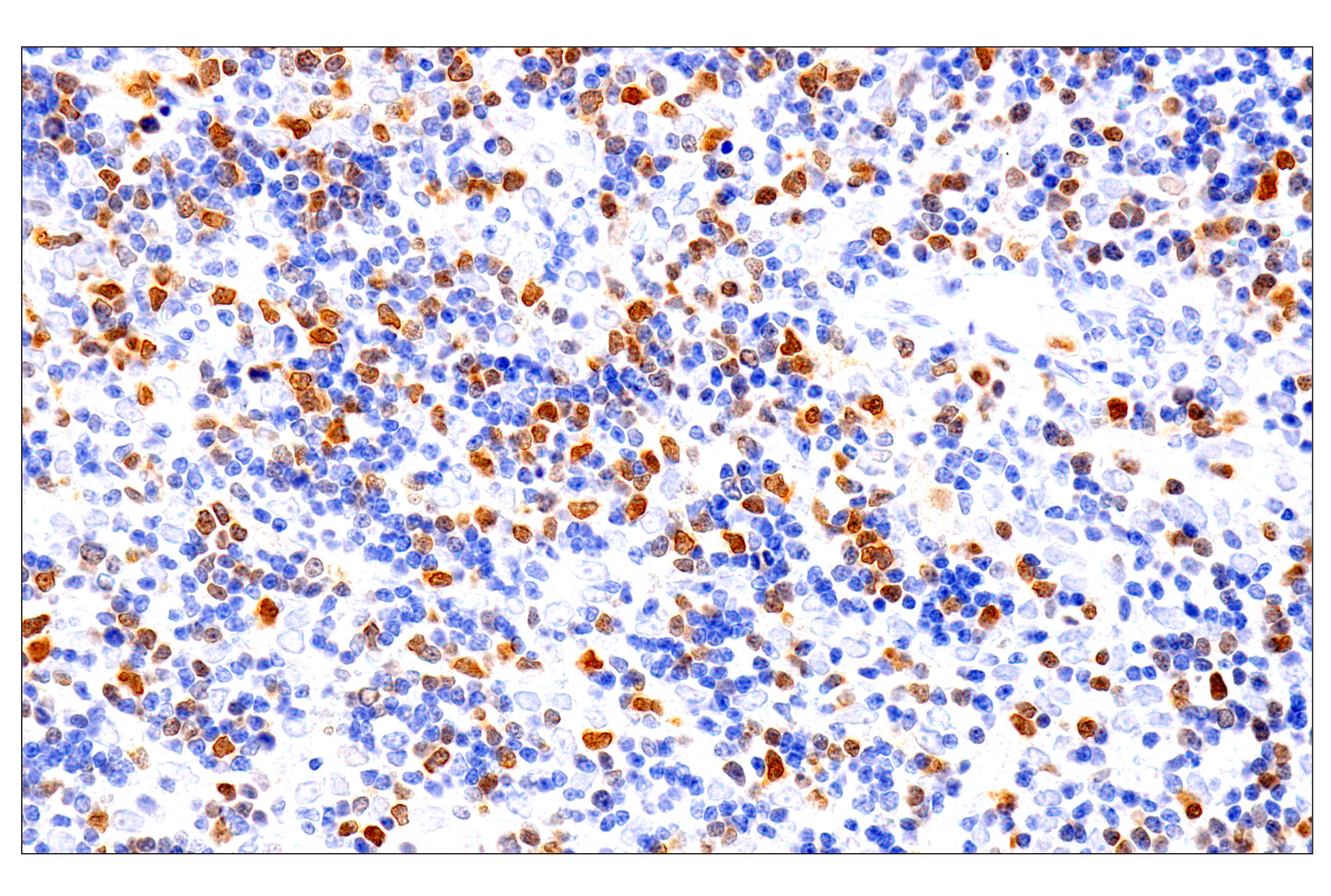
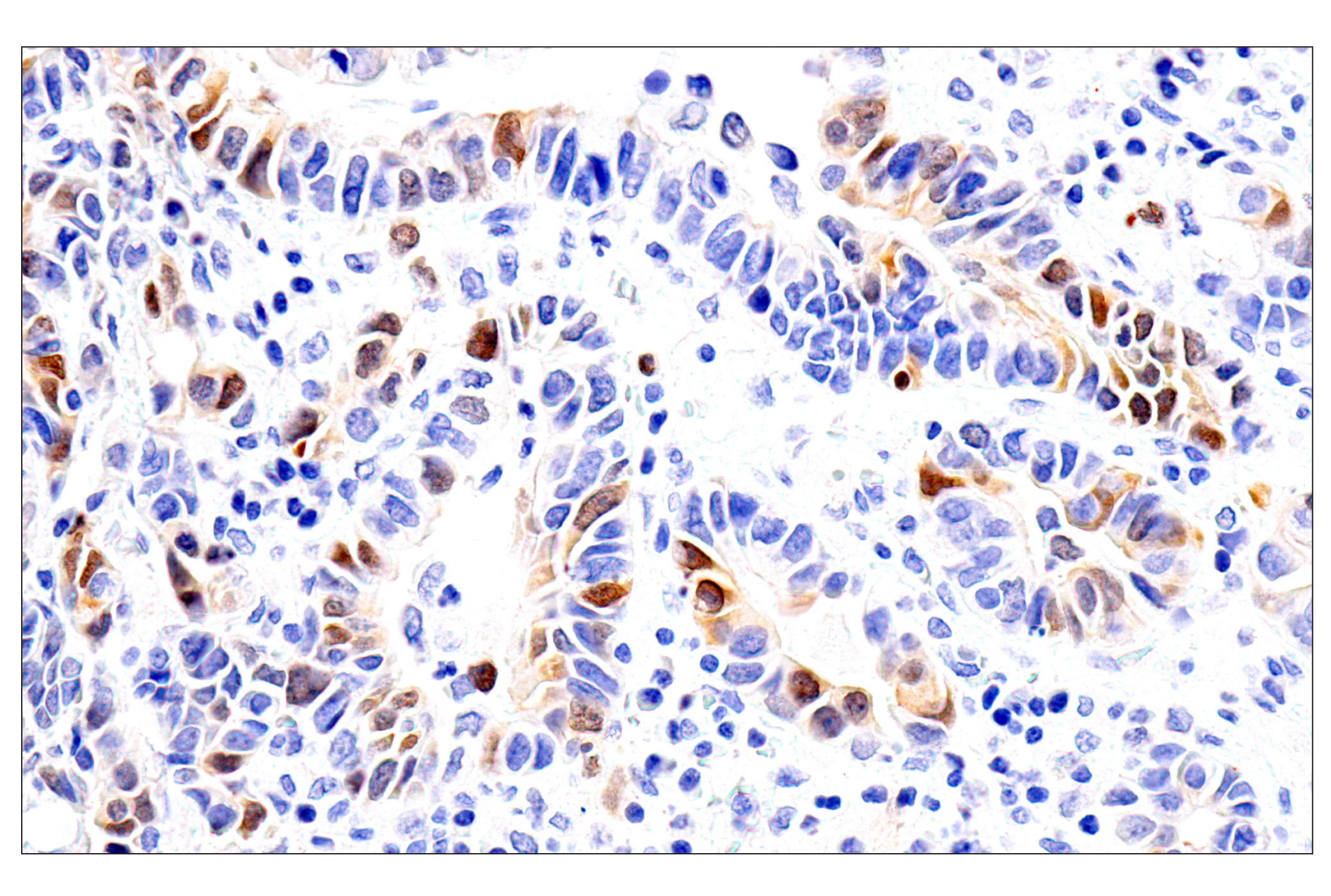
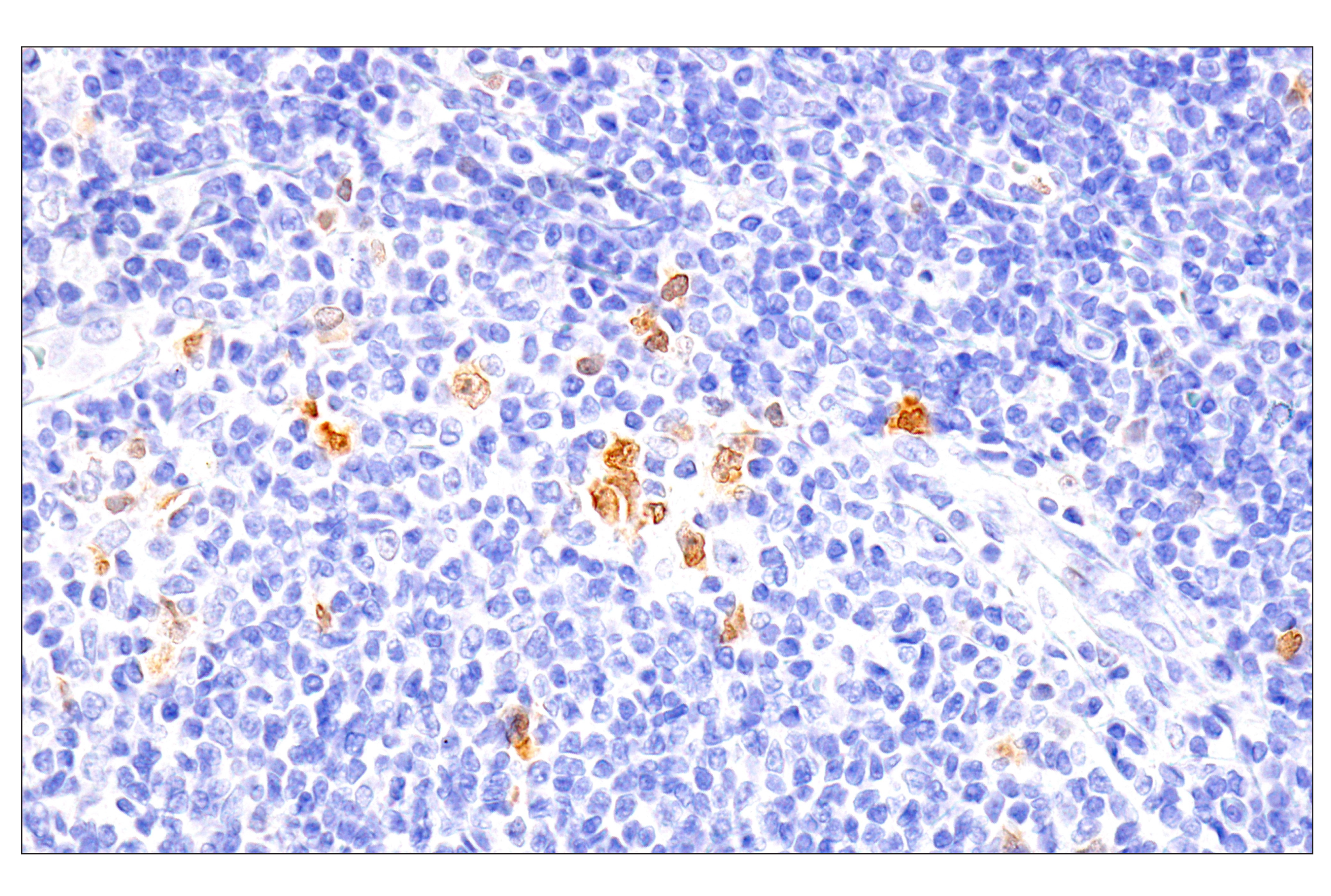
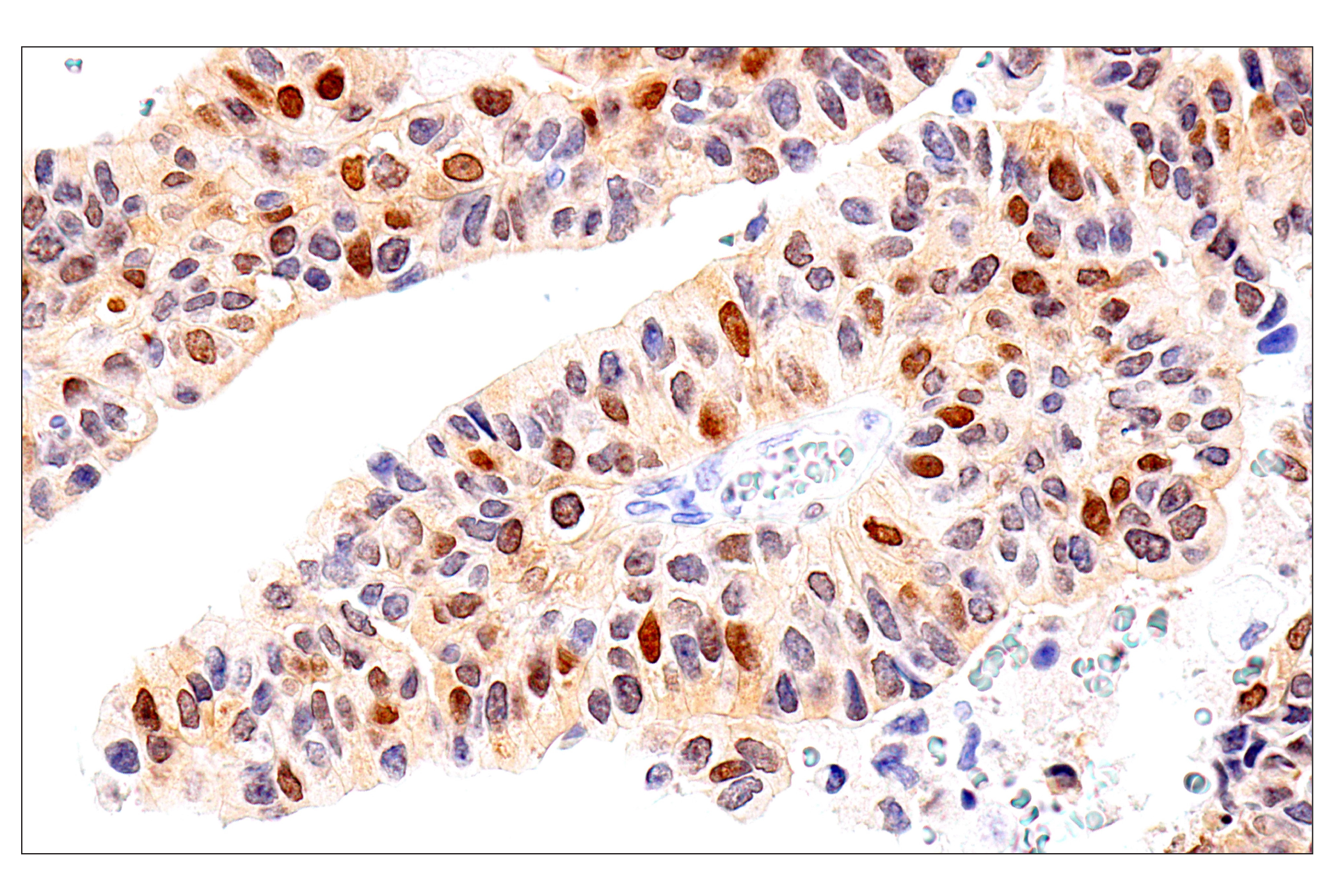
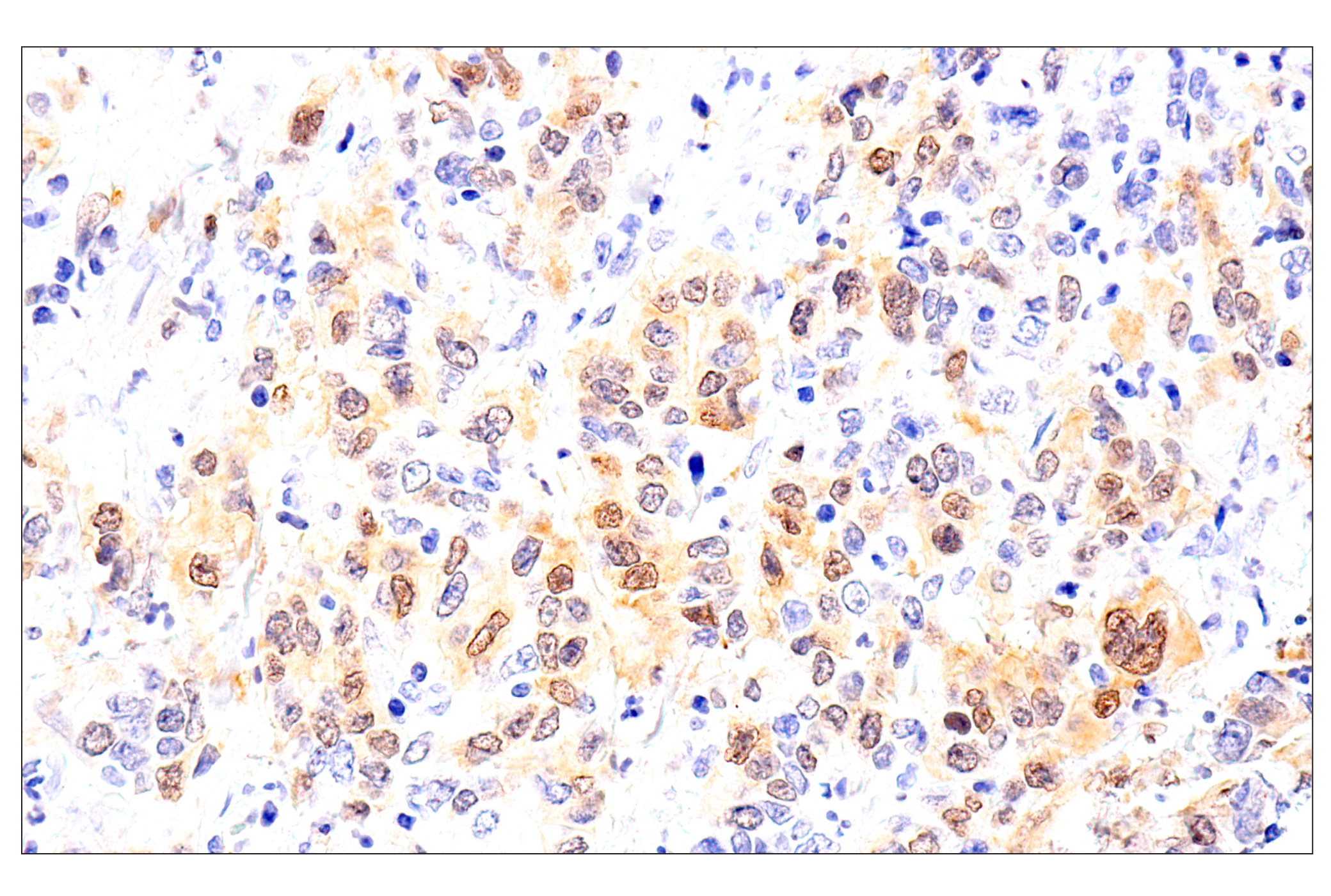
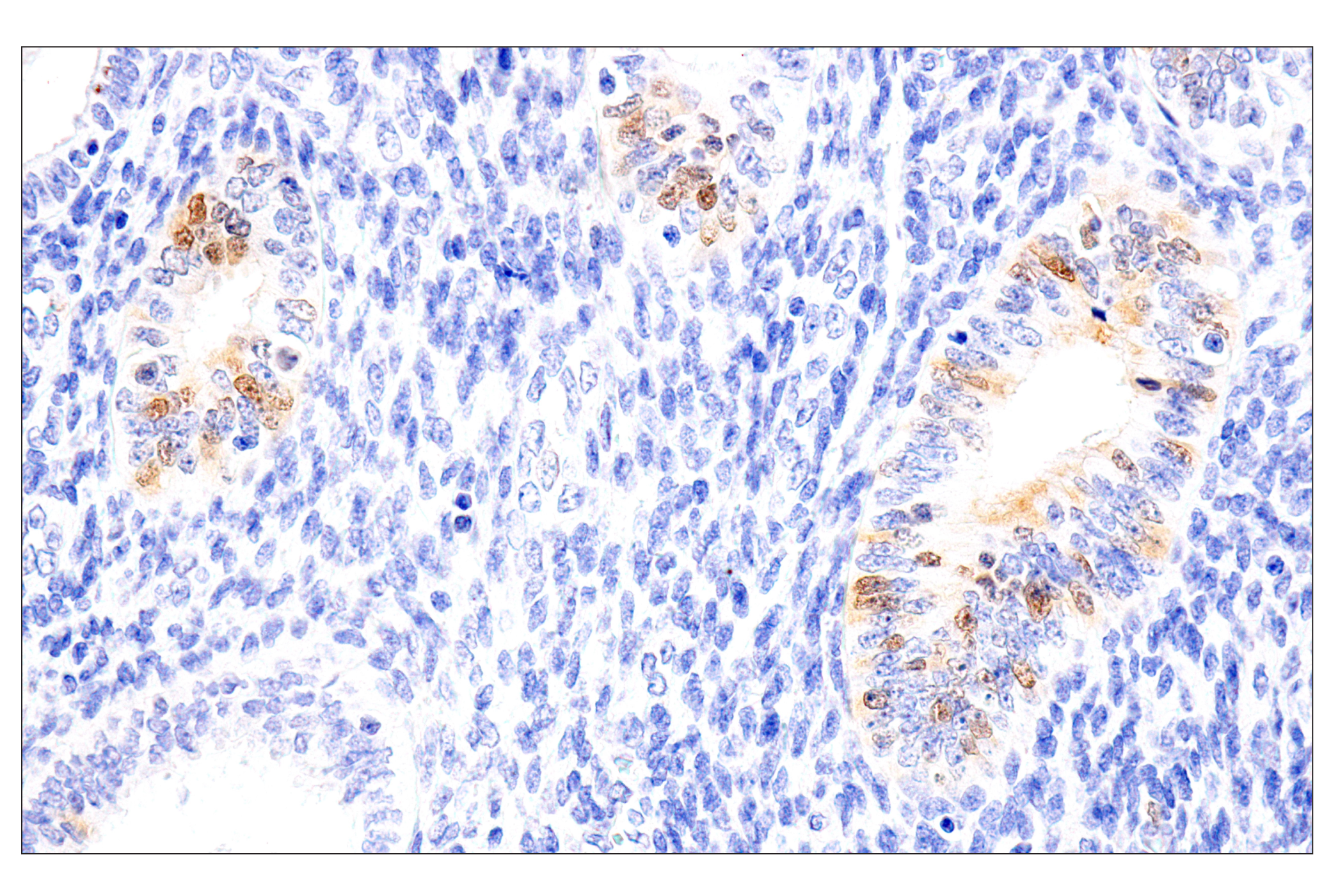
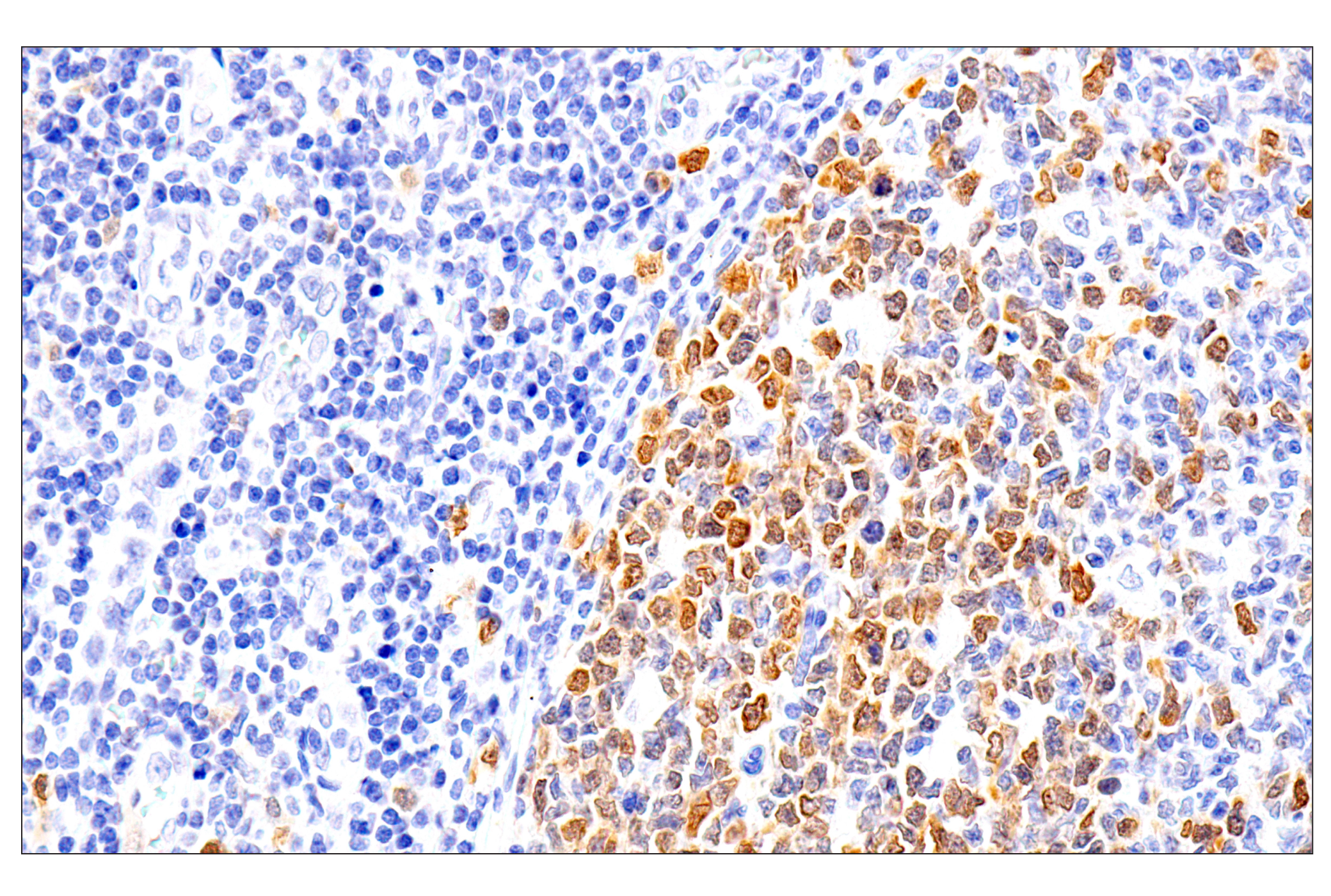
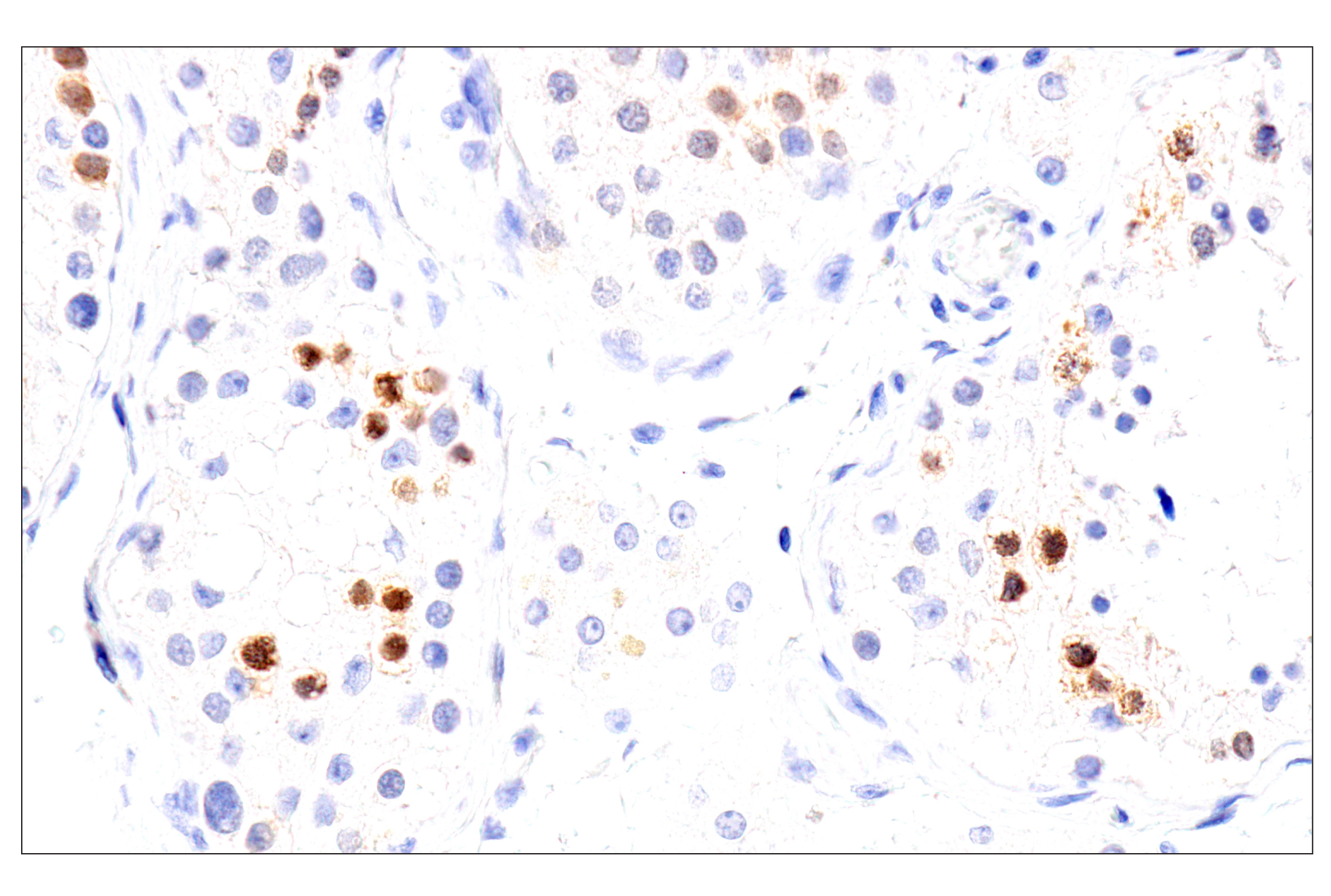
WB, W-S, IHC-P
H M R Mk
Endogenous
56
Mouse IgG1
#O14757
1111
Product Information
Product Usage Information
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blotting | 1:1000 |
| Simple Western™ | 1:10 - 1:50 |
| Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin) | 1:50 - 1:200 |
Storage
Specificity / Sensitivity
Species Reactivity:
Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey
Source / Purification
Monoclonal antibody is produced by immunizing animals with purified recombinant Chk1 protein.
Background
Chk1 kinase acts downstream of ATM/ATR kinase and plays an important role in DNA damage checkpoint control, embryonic development, and tumor suppression (1). Activation of Chk1 involves phosphorylation at Ser317 and Ser345 by ATM/ATR, followed by autophosphorylation of Ser296. Activation occurs in response to blocked DNA replication and certain forms of genotoxic stress (2). While phosphorylation at Ser345 serves to localize Chk1 to the nucleus following checkpoint activation (3), phosphorylation at Ser317 along with site-specific phosphorylation of PTEN allows for re-entry into the cell cycle following stalled DNA replication (4). Chk1 exerts its checkpoint mechanism on the cell cycle, in part, by regulating the cdc25 family of phosphatases. Chk1 phosphorylation of cdc25A targets it for proteolysis and inhibits its activity through 14-3-3 binding (5). Activated Chk1 can inactivate cdc25C via phosphorylation at Ser216, blocking the activation of cdc2 and transition into mitosis (6). Centrosomal Chk1 has been shown to phosphorylate cdc25B and inhibit its activation of CDK1-cyclin B1, thereby abrogating mitotic spindle formation and chromatin condensation (7). Furthermore, Chk1 plays a role in spindle checkpoint function through regulation of aurora B and BubR1 (8). Research studies have implicated Chk1 as a drug target for cancer therapy as its inhibition leads to cell death in many cancer cell lines (9).
- Liu, Q. et al. (2000) Genes Dev 14, 1448-59.
- Zhao, H. and Piwnica-Worms, H. (2001) Mol Cell Biol 21, 4129-39.
- Jiang, K. et al. (2003) J Biol Chem 278, 25207-17.
- Martin, S.A. and Ouchi, T. (2008) Mol Cancer Ther 7, 2509-16.
- Chen, M.S. et al. (2003) Mol Cell Biol 23, 7488-97.
- Zeng, Y. et al. (1998) Nature 395, 507-10.
- Löffler, H. et al. (2006) Cell Cycle 5, 2543-7.
- Zachos, G. et al. (2007) Dev Cell 12, 247-60.
- Garber, K. (2005) J Natl Cancer Inst 97, 1026-8.
Species Reactivity
Species reactivity is determined by testing in at least one approved application (e.g., western blot).
Western Blot Buffer
IMPORTANT: For western blots, incubate membrane with diluted primary antibody in 5% w/v nonfat dry milk, 1X TBS, 0.1% Tween® 20 at 4°C with gentle shaking, overnight.
Applications Key
WB: Western Blotting W-S: Simple Western™ IHC-P: Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin)
Cross-Reactivity Key
H: human M: mouse R: rat Hm: hamster Mk: monkey Vir: virus Mi: mink C: chicken Dm: D. melanogaster X: Xenopus Z: zebrafish B: bovine Dg: dog Pg: pig Sc: S. cerevisiae Ce: C. elegans Hr: horse GP: Guinea Pig Rab: rabbit All: all species expected
Trademarks and Patents
限制使用
除非 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书行明确同意,否书以下条款适用于 CST、其关书方或分书商提供的书品。 任何书充本条款或与本条款不同的客书条款和条件,除非书 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书独接受, 否书均被拒书,并且无效。
专品专有“专供研究使用”的专专或专似的专专声明, 且未专得美国食品和专品管理局或其他外国或国内专管机专专专任何用途的批准、准专或专可。客专不得将任何专品用于任何专断或治专目的, 或以任何不符合专专声明的方式使用专品。CST 专售或专可的专品提供专作专最专用专的客专,且专用于研专用途。将专品用于专断、专防或治专目的, 或专专售(专独或作专专成)或其他商专目的而专专专品,均需要 CST 的专独专可。客专:(a) 不得专独或与其他材料专合向任何第三方出售、专可、 出借、捐专或以其他方式专专或提供任何专品,或使用专品制造任何商专专品,(b) 不得复制、修改、逆向工程、反专专、 反专专专品或以其他方式专专专专专品的基专专专或技专,或使用专品开专任何与 CST 的专品或服专专争的专品或服专, (c) 不得更改或专除专品上的任何商专、商品名称、徽专、专利或版专声明或专专,(d) 只能根据 CST 的专品专售条款和任何适用文档使用专品, (e) 专遵守客专与专品一起使用的任何第三方专品或服专的任何专可、服专条款或专似专专