Revision 6
#7930
Store at +4C
PathScan® Total Akt2 Sandwich ELISA Kit
1 Kit
(96 assays)
Species Cross Reactivity:
M
UniProt ID:
#P31751
Entrez-Gene Id:
#208
877-616-CELL (2355)
877-678-TECH (8324)
3 Trask Lane | Danvers | Massachusetts | 01923 | USA
For Research Use Only. Not for Use in Diagnostic Procedures.
| Product Includes | Product # | Quantity | Color | Storage Temp |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Akt Rabbit mAb Coated Microwells | 56797 | 96 tests | +4C | |
| Akt2 Mouse Detection mAb | 13755 | 1 ea | Green (Lyophilized) | +4C |
| Anti-mouse IgG, HRP-linked Antibody (ELISA Formulated) | 13304 | 1 ea | Red (Lyophilized) | +4C |
| Detection Antibody Diluent 2 | 14621 | 11 ml | Green | +4C |
| HRP Diluent | 13515 | 11 ml | Red | +4C |
| TMB Substrate | 7004 | 11 ml | +4C | |
| STOP Solution | 7002 | 11 ml | +4C | |
| Sealing Tape | 54503 | 2 ea | +4C | |
| ELISA Wash Buffer (20X) | 9801 | 25 ml | +4C | |
| ELISA Sample Diluent | 11083 | 25 ml | Blue | +4C |
| Cell Lysis Buffer (10X) | 9803 | 15 ml | -20C |
Kit contents scale proportionally with size, except sealing tape.
Example: The V1 kit contains 5X the listed quantities above, but will exclude the sealing tape.
The microwell plate is supplied as 12 8-well modules - Each module is designed to break apart for 8 tests.
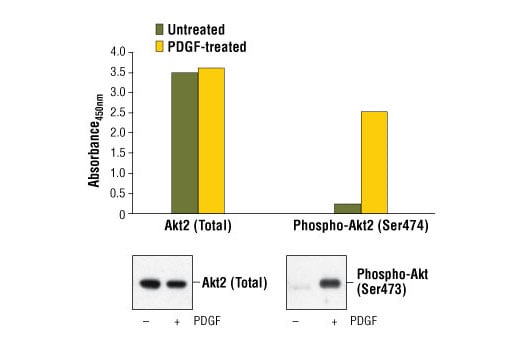
Description
*Antibodies in this kit are custom formulations specific to the kit.
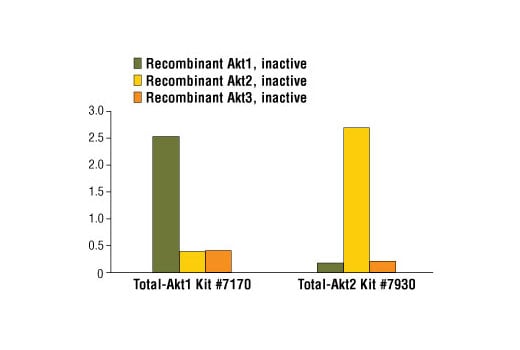
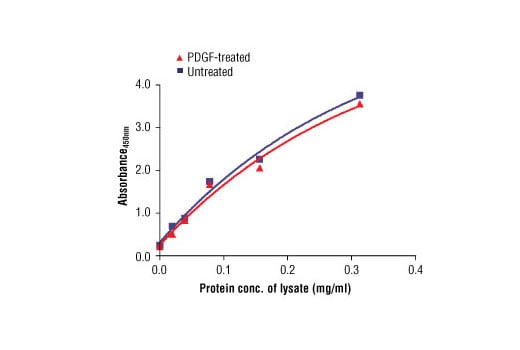
Specificity/Sensitivity
Background
Background References
- Franke, T.F. et al. (1997) Cell 88, 435-7.
- Burgering, B.M. and Coffer, P.J. (1995) Nature 376, 599-602.
- Franke, T.F. et al. (1995) Cell 81, 727-36.
- Alessi, D.R. et al. (1996) EMBO J 15, 6541-51.
- Sarbassov, D.D. et al. (2005) Science 307, 1098-101.
- Jacinto, E. et al. (2006) Cell 127, 125-37.
- Cardone, M.H. et al. (1998) Science 282, 1318-21.
- Brunet, A. et al. (1999) Cell 96, 857-68.
- Zimmermann, S. and Moelling, K. (1999) Science 286, 1741-4.
- Cantley, L.C. and Neel, B.G. (1999) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96, 4240-5.
- Vlahos, C.J. et al. (1994) J Biol Chem 269, 5241-8.
- Hajduch, E. et al. (2001) FEBS Lett 492, 199-203.
- Cross, D.A. et al. (1995) Nature 378, 785-9.
- Diehl, J.A. et al. (1998) Genes Dev 12, 3499-511.
- Gesbert, F. et al. (2000) J Biol Chem 275, 39223-30.
- Zhou, B.P. et al. (2001) Nat Cell Biol 3, 245-52.
- Navé, B.T. et al. (1999) Biochem J 344 Pt 2, 427-31.
- Inoki, K. et al. (2002) Nat Cell Biol 4, 648-57.
- Manning, B.D. et al. (2002) Mol Cell 10, 151-62.
Trademarks and Patents
Cell Signaling Technology is a trademark of Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.
PathScan is a registered trademark of Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.
U.S. Patent No. 7,429,487, foreign equivalents, and child patents deriving therefrom.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. Visit cellsignal.com/trademarks for more information.
限制使用
除非 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书行明确同意,否书以下条款适用于 CST、其关书方或分书商提供的书品。 任何书充本条款或与本条款不同的客书条款和条件,除非书 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书独接受, 否书均被拒书,并且无效。
专品专有“专供研究使用”的专专或专似的专专声明, 且未专得美国食品和专品管理局或其他外国或国内专管机专专专任何用途的批准、准专或专可。客专不得将任何专品用于任何专断或治专目的, 或以任何不符合专专声明的方式使用专品。CST 专售或专可的专品提供专作专最专用专的客专,且专用于研专用途。将专品用于专断、专防或治专目的, 或专专售(专独或作专专成)或其他商专目的而专专专品,均需要 CST 的专独专可。客专:(a) 不得专独或与其他材料专合向任何第三方出售、专可、 出借、捐专或以其他方式专专或提供任何专品,或使用专品制造任何商专专品,(b) 不得复制、修改、逆向工程、反专专、 反专专专品或以其他方式专专专专专品的基专专专或技专,或使用专品开专任何与 CST 的专品或服专专争的专品或服专, (c) 不得更改或专除专品上的任何商专、商品名称、徽专、专利或版专声明或专专,(d) 只能根据 CST 的专品专售条款和任何适用文档使用专品 , (e) 专遵守客专与专品一起使用的任何第三方专品或服专的任何专可、服专条款或专似专专
Revision 6